Figure 8. The Fli-1 transactivating compounds induce growth arrest and differentiation of erythroleukemic cells through PKC and, in part, through MAPK/ERK activation.
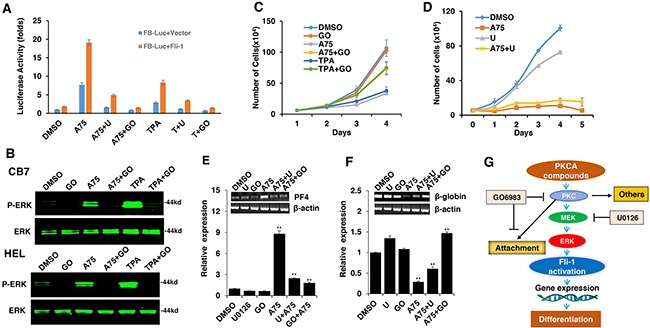
A. HEK293T cells co-transfected with FB-Luc and MigR1-Fli-1, and treated with A75 or TPA (1μM), show induction of Fli-1 transcriptional activity that can be blocked by U1026 (5μM) or GO6982 (2μM). B. Treatment of HEL or CB7 cells with A75 or TPA (2μM) induces MAPK/ERK phosphorylation that can be suppressed by GO6982 (2μM). C. Growth suppression induced by A75 or TPA (2μM) in HEL cells is reversed by GO6983 (2μM). D. Growth suppression induced in CB7 cells by A75 (2μM) is only marginally inhibited by U1026 (10μM). E, F. In CB7 cells, induction of megakaryocytic marker PF4 by A75 is completely inhibited by U0126 and GO6983 (5μM); these inhibitors suppressed downregulation of erythroid β-globin by A75. G. A model depicting the sequential events that occur in leukemic cells after treatment with PKCA compounds leading to Fli-1 transcriptional activation. PKCA compounds activate Fli-1 and also increase cell attachment independently of MAPK/ERK activation. PKCA compounds likely activate other pathways that further increase their growth inhibitory activity.
