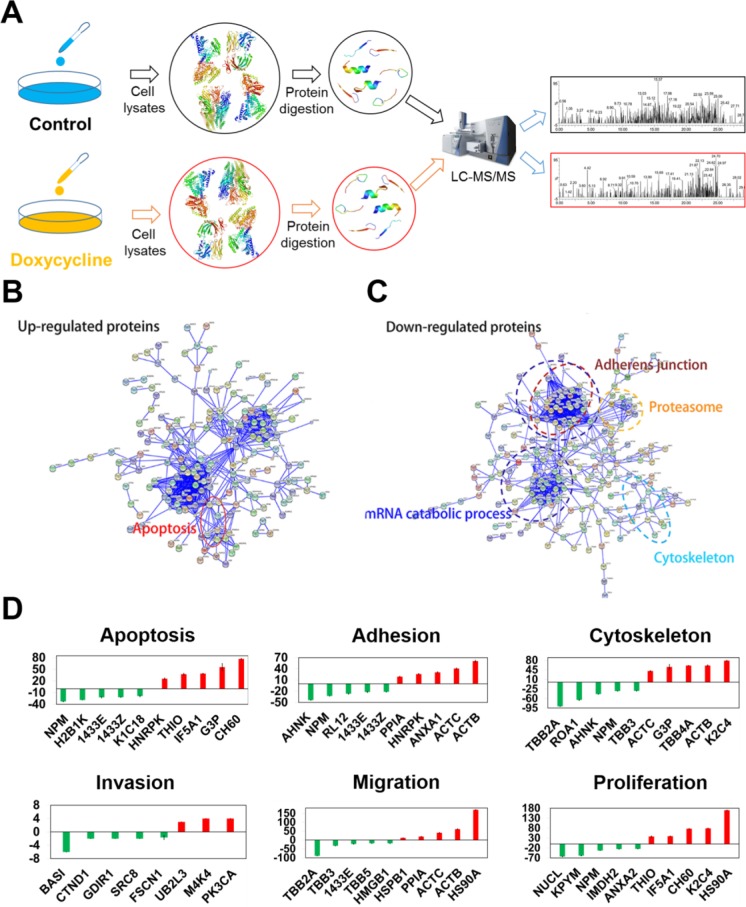
Figure 4. Differentially expressed proteins evaluated using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry revealed key biological functions influenced by doxycycline.
Among the 231 differentially expressed proteins, 101 were increased, and 130 were decreased. (A) Workflow of the proteomics analysis. (B, C). Protein-protein interaction networks of differentially expressed proteins. Significantly changed proteins correlated with apoptosis, adherens junctions, the proteasome, mRNA catabolic processes and the cytoskeleton. (D) Pathways perturbed in a doxycycline-dependent manner were associated with apoptosis, adhesion, the cytoskeleton, migration, proliferation and invasion. Results were obtained from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, and the error bars represent the standard deviation (*P < 0.05, *P < 0.01). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.