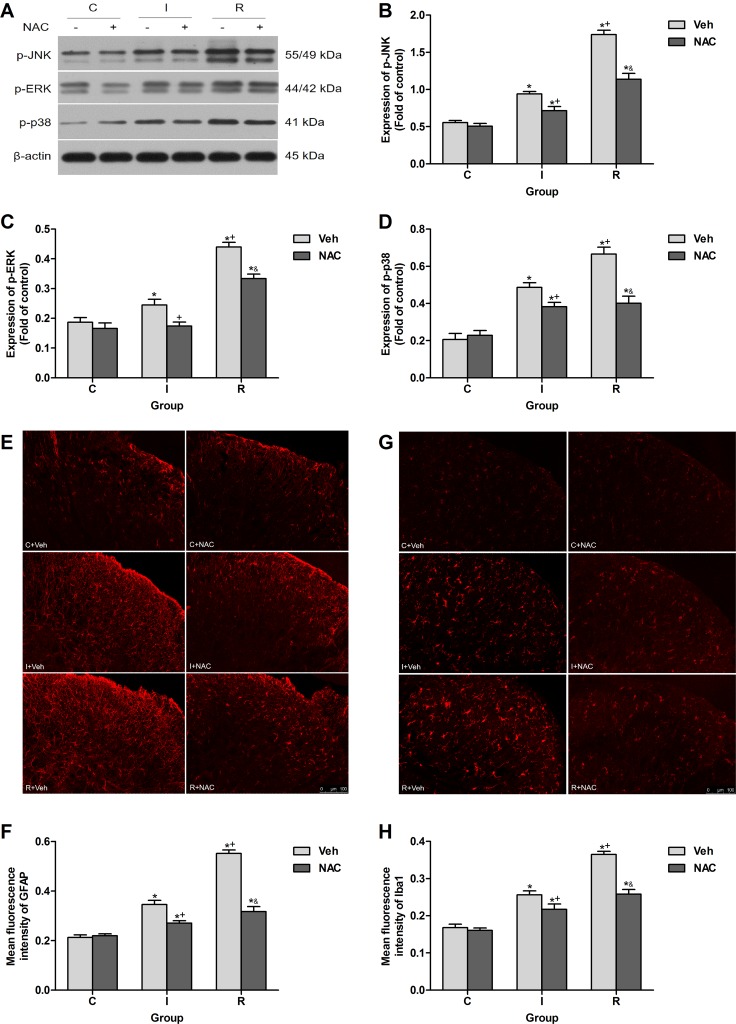
Figure 5. NAC inhibited remifentanil-induced spinal MAPK family phosphorylation and glial activation in ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn.
(A) Western blotting for p-JNK, p-ERK, p-p38 and β-actin resulted in products of 55/49, 44/42, 41 and 43 kDa. (B–D) Densitometric quantification of p-JNK, p-ERK and p-p38 immunoreactivity on Western blots. β-actin was used as a loading control (n = 5). (E and F) Images and quantification of immunofluorescence showing GFAP in the ipsilateral dorsal horns. (G and H) Images and quantification of immunofluorescence showing Iba1 in the ipsilateral dorsal horns. Quantification of immunofluorescence was presented as mean fluorescence intensity in the superficial dorsal horns (n = 5). The ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord was collected and analyzed 2 h after intraperitoneal injection. Values expressed as mean ± SD. The treatment style was the same as described in Figure 3. Significant difference was revealed after One-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05 compared with group C+Veh, +P < 0.05 compared with group I+Veh, &P < 0.05 compared with group R+Veh, Bonferroni post hoc tests).