Figure 6. Example interventional treatments for neuropathic pain. a.
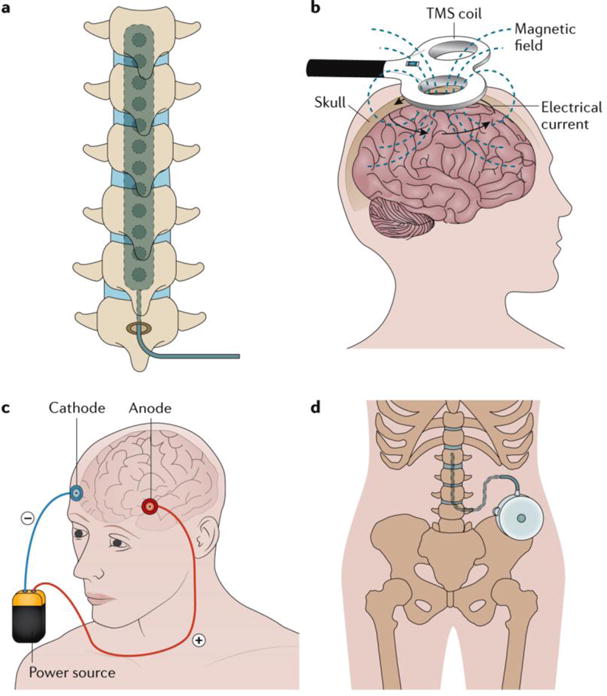
Spinal cord stimulation traditionally applies a monophasic square-wave pulse (at a frequency in the 30–100 Hz range) that results in paraesthesia in the painful region. b | Cortical stimulation involves the stimulation of the pre-central motor cortex below the motor threshold using either invasive epidural or transcranial non-invasive techniques (such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation). c | Deep brain stimulation uses high-frequency chronic intracranial stimulation of the internal capsule, various nuclei in the sensory thalamus, periaqueductal and periventricular grey, motor cortex, septum, nucleus accumbens, posterior hypothalamus and anterior cingulate cortex as potential brain targets for pain control. d | Intrathecal treatments provide a targeted drug delivery option in patients with severe and otherwise refractory chronic pain. The pumps can be refilled through an opening at the skin surface.
