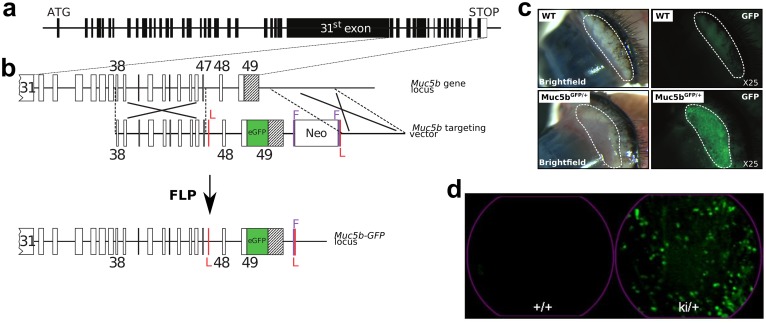
Fig 3. Strategy for creating Muc5b-GFP knock-in (KI) mice and fluorescence stereo- and endomicroscopy.
(a) Muc5b gene structure. Human and mouse Muc5b are composed of 49 exons indicated by rectangles (black, coding sequence and white, 3’UTR) and introns by lines. The large 31st exon carries the sequences encoding peptides enriched in Ser+Thr+Pro. The initiation (ATG) and STOP codons are indicated. (b) Strategy for replacing the unique STOP codon of the endogenous mouse Muc5b gene with an enhanced GFP sequence (in green). A Gly-Ser-Ile-Ala-Thr linker is placed between the last amino acid of Muc5b and a synthetic sequence coding for a monomeric enhanced GFP sequence. Exons are indicated by rectangles and few of them are numbered. The unique 3’UTR region in black belongs to the 49th and last exon. The targeting vector contains 3.2-kb of upstream (exons 38–47) and 2.2-kb of downstream sequences from the mouse Muc5b locus. LoxP sites (red vertical lines), which played no role in these experiments, flank the two last exons of Muc5b. A Neo positive selectable marker for embryonic stem cell integration flanked by two FRT sites (purple vertical lines) was inserted downstream of the Muc5b locus. The Muc5b-GFP line was obtained by crossing mice with a Flpe recombinase-expressing mouse in order to delete the neomycin cassette used for selection in embryonic stem cells. (c) Representative examples of pictures in bright-field mode and under GFP excitation by stereomicroscopy of fresh excised conjunctivas from wild-type (WT) and transgenic (Muc5bGFP/+) mice. (d) Extracted frames from representative movies from conjunctivas acquired by pCLE (see S1 Movie) from a WT (+/+) and a transgenic mouse (ki/+).