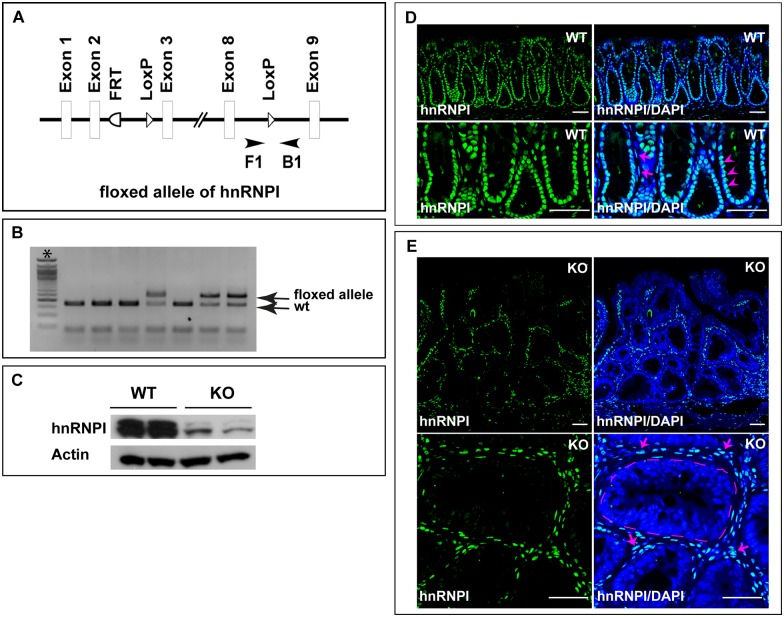
Fig 1. Generation of the IEC-specific hnRNPI knockout mice.
(A) A schematic representation shows the knockout strategy. A primer pair (F1 and B1) flanking one loxP site (arrowheads) was used for genotyping the IEC-specific hnRNPI knockout mice. (B) An example of genotyping PCR result shows the sizes of PCR products amplified from the hnRNPI floxed allele (236 bp) and wild-type allele (166 bp). *, 50bp DNA ladder. (C) Western blotting result shows efficient ablation of hnRNPI in the colonic epithelial cells of the knockout mice. hnRNPI protein levels from two knockout mice and two control sibling littermates are shown. (D) and (E) Immunofluorescence staining using an anti-hnRNPI antibody shows hnRNPI protein localization in the wild-type and hnRNPI knockout colon. Magnified images are shown in the lower panels. Nuclear accumulation of hnRNPI protein was detected in both colonic epithelial cells (arrowheads) and cells in the lamina propria (arrows) in wild-type mice (D). hnRNPI expression is diminished in the nuclei of colonic epithelial cells in the knockout mice, but remains unaffected in the lamina propria cells (E, arrows). Note the increased number of immune cells in the lamina propria of the knockout mice. The dotted line indicates the border of a centrally located crypt. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. WT, wild-type; KO, knockout. Scale bars, 50 μm.