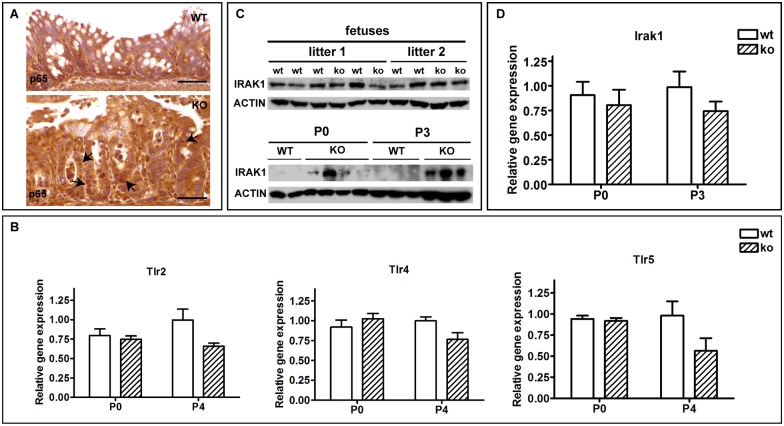
Fig 7. The IEC-specific hnRNPI knockout neonates display hyperactive NF-κB signaling and upregulation of IRAK1 protein expression in the colon.
(A) Immunohistochemical staining with an anti-p65 antibody shows p65 nuclear translocation in the colonic epithelium of the knockout mice at P3 (the bottom panel, arrows). (B) Real-time PCR results show that the expression of TLRs is not increased in the colon of the knockout mice at both P0 and P4. (C) Western blot shows IRAK1 protein expression is increased in the knockout colon at P0, and the increase of IRAK1 protein level is more prominent at P3. The IRAK1 protein level remains unchanged in the knockout fetal colon. Actin is served as the loading control. At least 3 litters of each age were tested and data shown are representative. (D) Real-time PCR result shows that the mRNA level of IRAK1 in colons of the knockout neonates is not upregulated at both P0 and P3. Data in B and D are presented as mean values relative to Gapdh (± s.e.m). N = 3–5 mice per group. The knockout group and the wild-type group are sibling littermates. At least 3 litters of each age were tested and data shown are representative. WT, wild-type; KO, knockout. Scale bars, 50 μm.