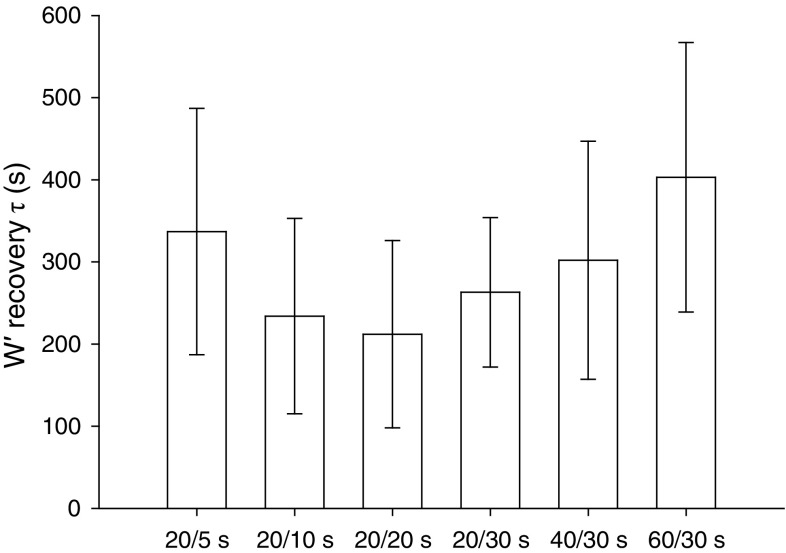
Fig. 6.
The influence of different work and recovery intervals during intermittent severe-intensity exercise on the time constant (τ) for W′ reconstitution. The mean ± standard deviation W′ recovery time constant tended to become shorter as the recovery duration separating 20-s work bouts was increased from 5 to 20 s. Conversely, the W′ recovery became progressively slower as the recovery duration was kept constant at 30 s, whereas the work duration was increased from 20 to 60 s. Figure re-drawn based on data from Skiba et al. [58]