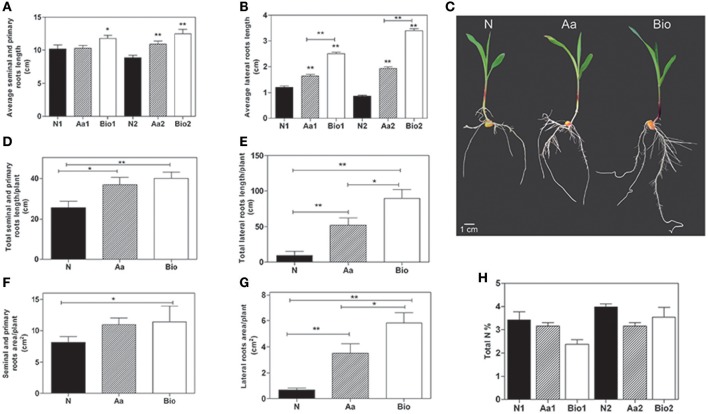
Figure 1.
Phenotypic analysis of maize roots after 3 days of treatment with inorganic nitrogen (N), amino acids (Aa), or protein hydrolysates (Bio). Average seminal and primary root length (A) and average lateral root length (B) of seedlings treated with protein hydrolysates (0.05 and 0.1 mlL−1) and seedlings treated with equivalent amounts of total N (5.65 and 11.3 mg L−1, respectively) supplied either as inorganic nitrogen (N) or as a mixture of free amino acids mimicking the composition in amino acids of the protein hydrolysate product. Root length was evaluated using ImageJ software (http://imagej.net). For lateral root length determination, the 10 longest roots were chosen manually. (C) Representative maize seedlings from N2, Aa2, and Bio2 treatments. Total length of seminal and primary roots (D), total length of lateral roots (E), total surface area of primary and seminal roots (F), and total surface of lateral roots (G) of seedlings treated with a concentration of protein hydrolysates, free amino acids and inorganic nitrogen equal to11.3 mgL−1 of total N measured with WinRHIZO™ software. (H) Total N content in roots of seedlings treated with protein hydrolysates, free amino acids and inorganic N at two doses. In (A,B,H) N1, Aa1, and Bio1 refer to the lowest N dose (5.65 mg L−1) and N2, Aa2, and Bio2 refer to the highest one (11.3 mg L−1). The average values are reported. Bars represent the standard error (SEM) [n = 24, except for data in (H), where n = 3], if not otherwise specified, Student's t-test was applied vs. N-treated plants, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.