Figure 4.
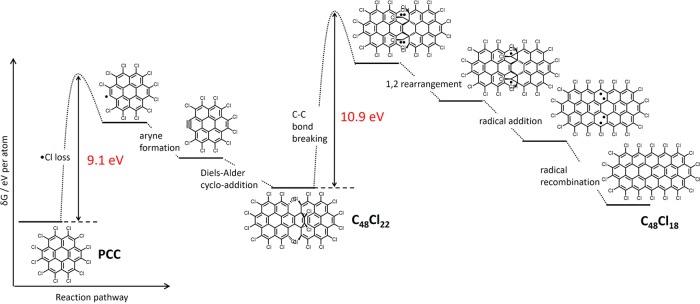
Energy profile of the intermolecular reactions observed for PCC in carbon nanotubes. Impact of the 80 keV e-beam causes dissociation of C–Cl bonds and the formation of a reactive aryne species (similar to the reaction of PCC observed on graphene). Provided that the space in the nanotube is sufficient for the aryne to reach a near-orthogonal orientation to a neighboring PCC molecule, the aryne (dienophile) and PCC (diene) undergo a Diels–Alder cycloaddition leading to the relatively stable C48Cl22 adduct. Under further e-beam irradiation, the initial adduct loses two Cl2 molecules and rearranges into a flat molecule C24Cl18 with an extended fully aromatic π-system.