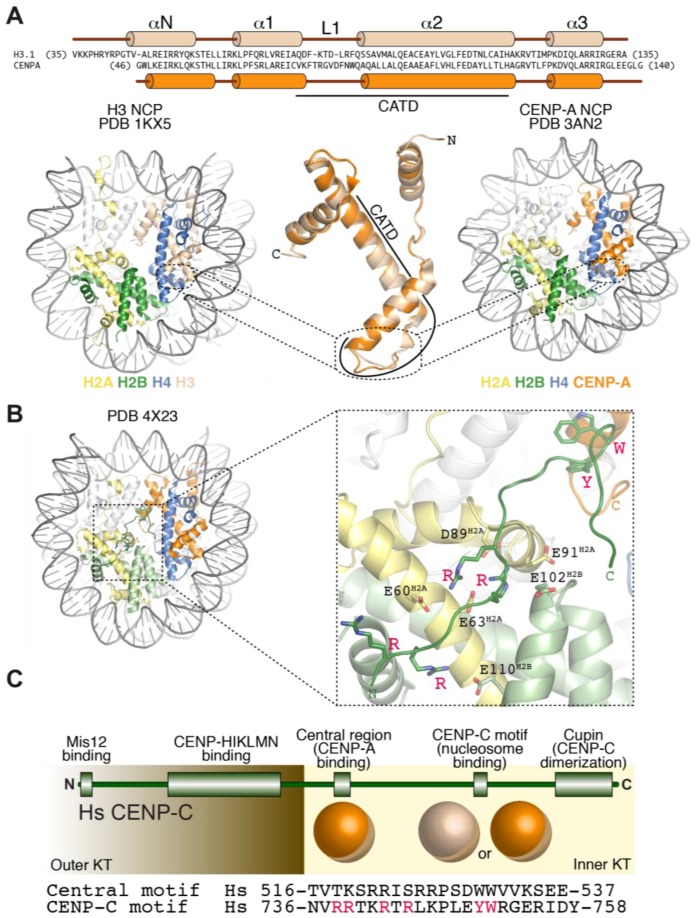
Figure 3.
The CENP-A nucleosome and its specific recognition by CENP-C. (A) Comparison of H3 and CENP-A primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. Sequence and structure changes concentrate in the N-terminal region, in the L1 segment of the CATD, and in the C-terminal region; (B) Structure of the complex of the CENP-C motif bound to a nucleosome containing a chimeric histone H3 with grafted hydrophobic C-terminal peptide of CENP-A [79]; (C) Scheme illustrating the organization of CENP-C as a “blueprint” for kinetochore assembly along the outer to inner kinetochore axis [80]. The H3 nucleosome structure is from X. laevis, the CENP-A nucleosome structure is human, and the CENP-C motif-bound structure has a Drosophila nucleosome core particle (in which the human CENP-A tail was grafted onto H3) bound to a rat CENP-C motif.