Figure 5.
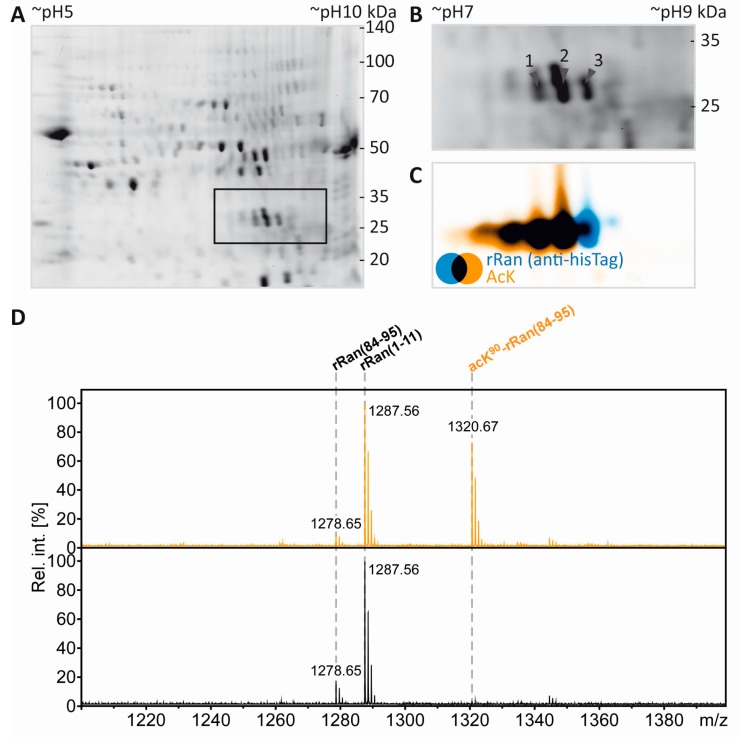
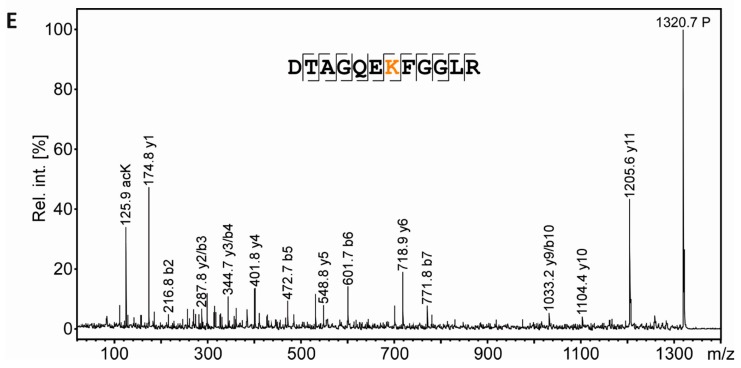
Separation and PTM mapping of rRAN proteoforms. A: Colloidal Coomassie-stained 2D-gel of myelin protein. Recombinant RAN (rRAN) specifically acetylated at K90 and non-acetylated rRAN spiked into the myelin sample immediately before IEF resulted in three additional protein spots. The box indicates the gel region shown in B. B: Gel region containing spots resulting from spiking of rRAN (labeled 1–3). C: Proteins were partially transferred onto PVDF-membrane and subjected to immunodetection using anti-AcK antibody (in orange) and anti-His-tag antibody (in blue), the latter detecting both, acetylated and non-acetylated, rRAN proteins. rRAN spots 1 and 2 show major acetylation as indicated by black color in overlay, whereas spot 3 contains rRAN, but only minor AcK signal. D: Zoom into the PMF spectra of rRAN peptides. The proteolytic peptide AcK90-rRAN(84–95) (m/z 1320.67) was prominent in spot 2 (upper panel), but virtually absent in spot 3 (lower panel). The corresponding non-acetylated peptide rRAN(84–95) (m/z 1278.65) was more abundant in spot 3 (lower panel) than in spot 2 (upper panel). The identity of all three peptides annotated was confirmed by mass spectrometric sequencing (only shown for AcK90-rRAN(84–95) in E. E: Sequencing of the proteolytic peptide AcK90-rRAN(84–95) by MS/MS. In the fragment ion mass spectrum, P denotes the precursor signal, and only b- and y-ions are labeled for the sake of clarity. On the basis of the conclusive N- and C-terminal ion series, acetylation was clearly assigned to K90. Mascot MS/MS ions score was 86 (identity threshold 31). Note that the signal at m/z 126 represents a signature immonium ion indicating the presence of AcK [71].