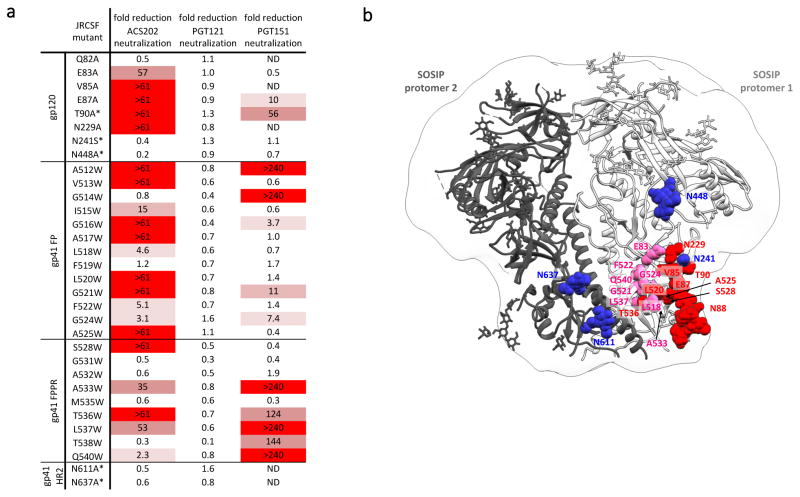
Figure 3. JR-CSF virus mutants affecting ACS202 neutralization.
(A) ACS202 neutralization of JR-CSF virus mutants containing the listed single amino-acid substitutions, with those that result in deletion of a glycan site indicated with an *. The values shown are the fold-reduction in neutralization titer for each mutant compared to the wild-type virus (n=3). The color-scheme is based on the intensity of the red shading increasing as the neutralization capacity decreases. The highest ACS202 concentration tested was 10 μg/ml and the IC50 value for ACS202 was 0.083 μg/ml. ND: not determined. FP: fusion peptide. FPPR: fusion peptide proximal region. HR2: Heptad repeat region 2.
(B) Mutations that affect the neutralization by ACS202 were modeled onto the crystal structure of BG505 SOSIP.664 trimers in complex with a putative precursor of the PGT121 family (PDB: 5cez). Residue labels denote the corresponding JR-CSF sequence at the modeled BG505 position. Mutations substantially reducing neutralization by ACS202 colored red and pink, while amino acids colored blue had no effect on neutralization when mutated.