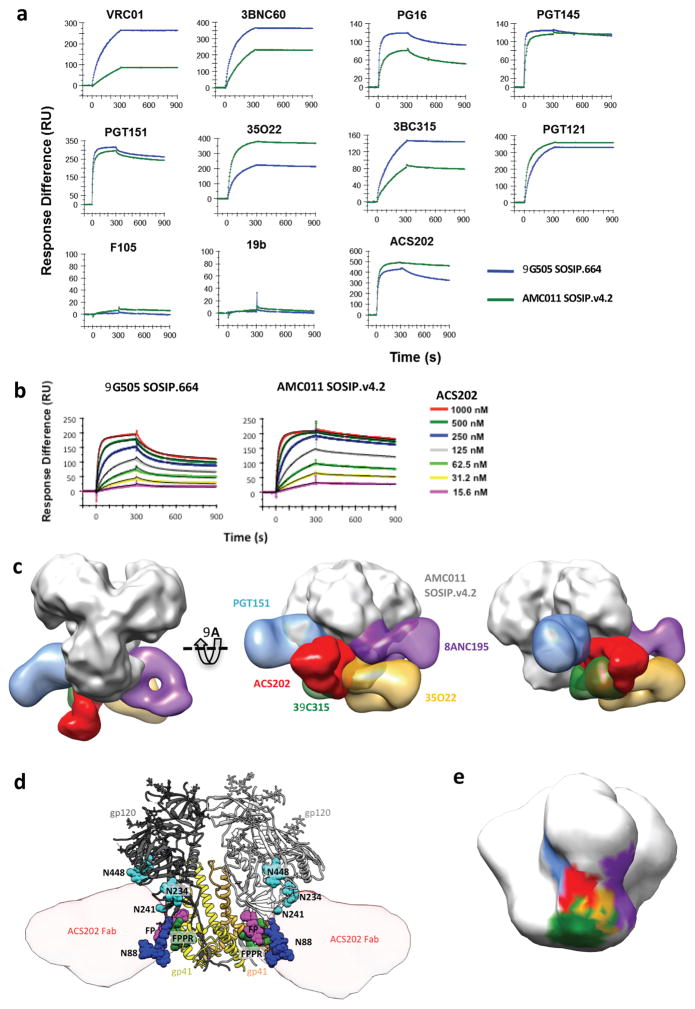
Fig. 5. Antigenicity of AMC011 SOSIP.v4.2 trimers and NS-EM imaging of their complex with ACS202.
(A) SPR was used to quantify the binding of the indicated bNAbs and non-NAbs (IgG, each at 500 nM) over a 300 s period to AMC011 SOSIP.v4.2 trimers (green) versus BG505 SOSIP.664 trimers (blue) (data displayed is representative of 2 individual experiments). (B) A dose-range analysis of ACS202-Fab binding to the same trimers (data displayed is representative of 2 individual experiments). (C) Docking of BG505 SOSIP.664 into the EM reconstruction of ACS202 in complex with AMC011 SOSIP.v4.2. Only the EM density for the ACS202 Fab is shown for clarity. The FP and FPPR regions are colored magenta and green, respectively. (E) To estimate the ACS202 epitope footprint, the crystal structure of anti-RSV antibody AM14 (PDB: 4zyk) was used as the two antibodies have a sequence homology of 80%. (F) 3D model of ACS202 in complex with SOSIP compared to nearby bNAb epitopes. UCSF Chimera 45 was used to dock published EM reconstructions of SOSIP-Fab complexes (PGT151: EMDB-5921; 35O22: EMDB-2672; 8ANC195: EMDB-2625; 3BC315: EMDB-3067) to an EM map constructed using the x-ray coordinates of ligand-free BG505 SOSIP.664 (PDB: 4zmj), low pass filtered to 30 Å. To display the relative docking of Fabs onto the EM reconstruction of AMC011 SOSIP.v4.2 trimers, the “segment map” option was used in UCSF Chimera to isolate the density of the Fab components alone.