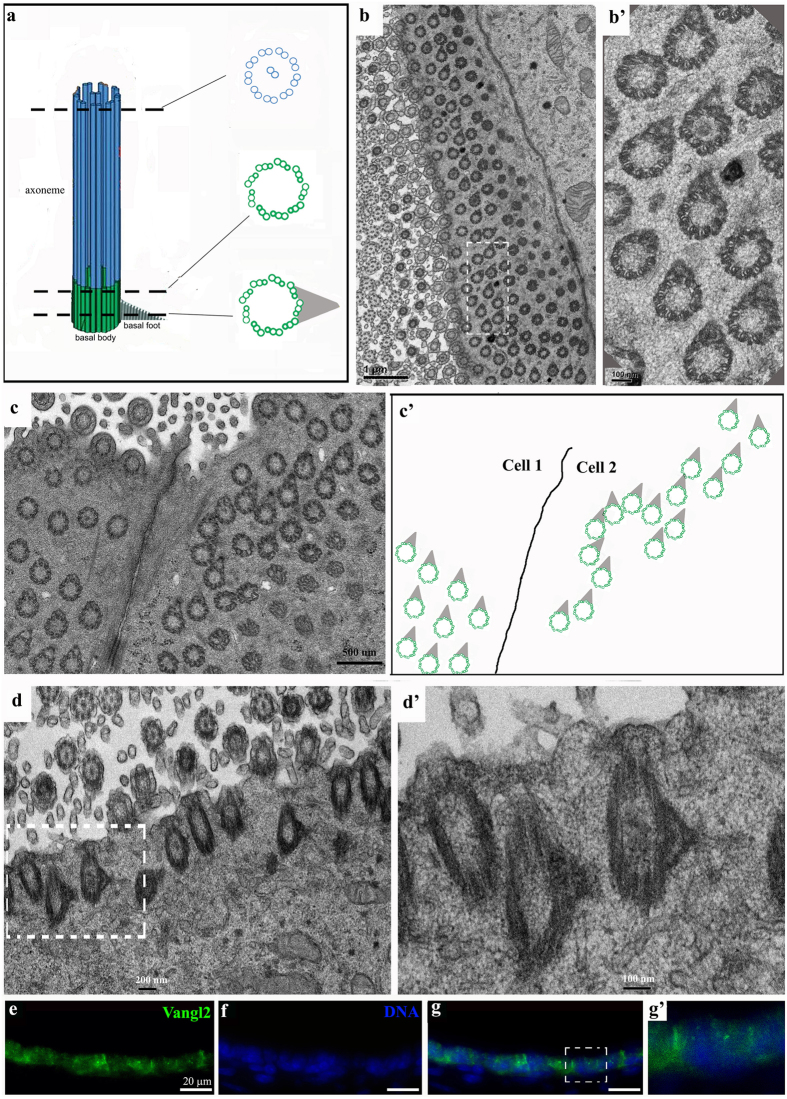
Figure 4. Planar cell polarity of the motile cilia in the middle ear.
(a) Diagram of microtubules and the basal body of a motile cilium. The ciliary axoneme consists of nine tubulin doublets and a central pair of tubulin doublets that is the hallmark of a motile cilium. The basal body is made up of nine tubulin triplets. At the level of the basal foot, accessory proteins compose a triangular electron-dense structure on transmission electron microscopy (TEM) graphs, which marks the orientation of the cilium. (b–d) Horizontal (b,b’,c,c’) and vertical (d,d’) TEM micrographs of the middle ear epithelium. TEM through the basal foot level revealed that cilia are oriented toward the same direction (b–d). b’ and d’ are a large view of the boxed regions in (b and d) respectively. (c’) marks the orientation of basal feet when their orientation was visible in c. Scale bars: 1 μm (b), 100 nm (b’), 500 nm (c), 200 nm (d) and 100 nm (d’). (e–g) A cryosection of the middle ear staining with an antibody against Vangl2 (green) and DNA (Hoechst, blue). (g’) is a larger view of the boxed region in (g). Vangl2 is enriched at the apical cortex. Scale: 20 μm.