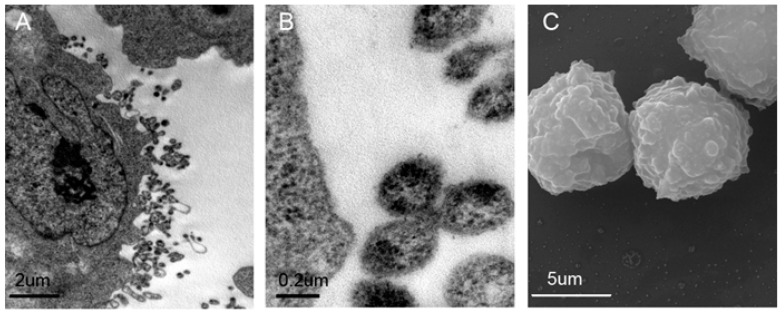
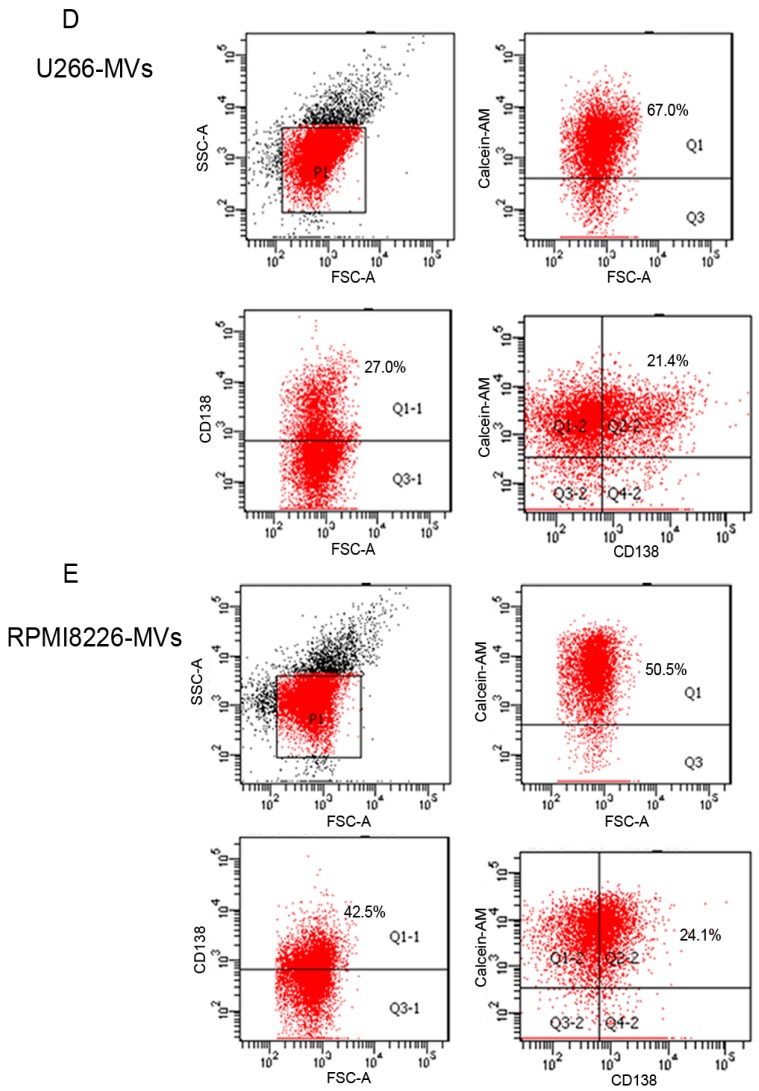
Figure 1.
Characterization of myeloma cell-derived microvesicles (MM-MVs) (A,B) Transmission electron microscopy revealing MVs (arrow) as 100–1000 μm vesicles shed from U266 cells (U266-MVs). Scale bar = 2 μm (A) and 0.2 μm (B); (C) Scanning electron microscopy showing typical morphology of MVs derived from RPMI8226 myeloma cells (RPMI8226-MVs). Scale bar = 2 μm; (D,E) Representative flow cytometry analysis of U266-MVs and RPMI8226-MVs revealing the presence of CD138+Calcein-AM+ vesicles, with the 1 μm microbeads for gating the MVs for size verification and Calcein-AM to detect the integrity of MVs.