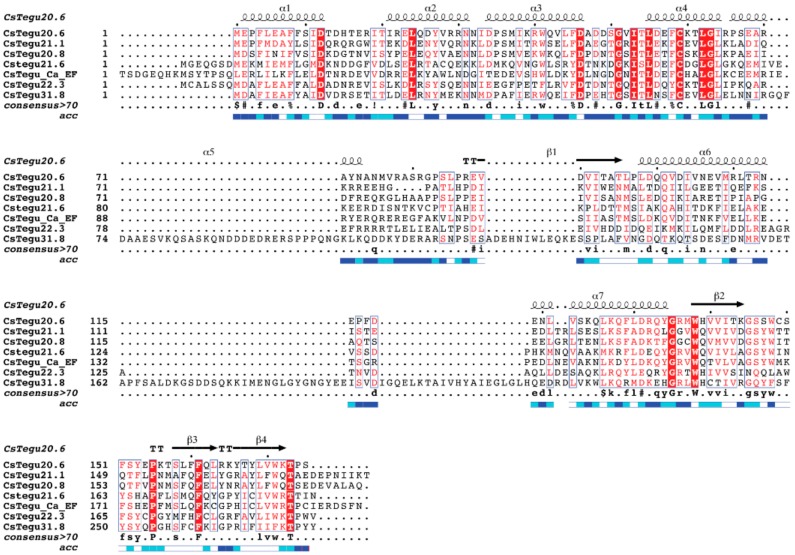
Figure 1.
Comparison of amino acid sequence of the 20.6-kDa tegumental protein of C. sinensis (CsTegu20.6) with other C. sinensis tegumental proteins. Multiple sequences alignment was visualized by ESPript [21] after alignment of the protein sequences using MAFFT [22]. Secondary structure features of CsTegu20.6 are given above the alignments. α-helices and β-strands are represented as helices and arrows, respectively, and β-turns are marked with TT. Conserved areas are shown shaded. Conserved sequences are indicated by a box if more than 70% of the residues are similar. The similar sequences are indicated by colored background considering physico-chemical properties. “acc” indicates the relative accessibility of each residue. The blue square scale is set as follows: “accessible” (blue, 0.4 < A ≤ 1.0), “intermediate” (cyan, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 0.4) and “buried” (white, A < 0.1). Accession numbers of the sequences presented are as follows: CsTegu21.1 (ADZ13689.1), CsTegu20.8 (ABC47326.1), CsTegu21.6 (JF911532), CsTegu_Ca (ABZ82044), CsTegu22.3 (ABK60085.1) and CsTegu31.8 (ABK60086.1).