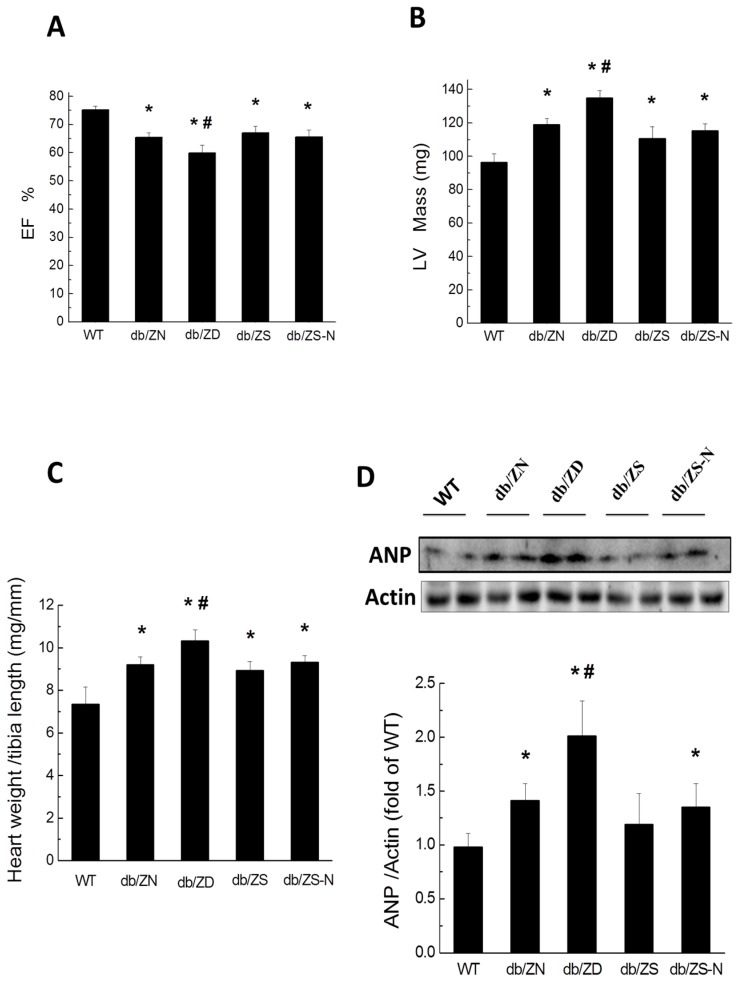
Figure 2.
Zn deficiency exacerbates diabetic-induced heart hypertrophy and function. Animals were treated as described in Figure 1. EF% (A) and corrected Left ventricular (LV) mass (mg/g) (B) were examined by echocardiography. Heart-weight to tibial length ratio (C) and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) protein levels obtained by Western Blot (D) were assessed as indicators of heart hypertrophy and function. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 4–7, details in Figure 1). *, p < 0.05 vs. WT group; #, p < 0.05 vs. db/ZN group.