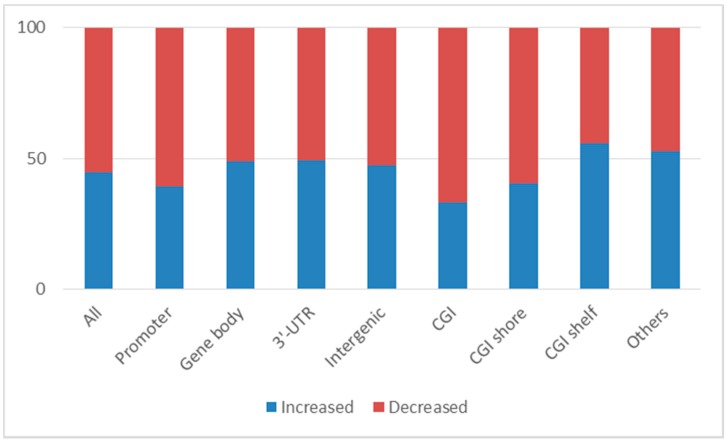
Figure 1.
The proportions of CpG sites which showed increased or decreased DNA methylation changes after clozapine treatment. Of 29,134 significant CpG sites, clozapine caused an increased DNA methylation at 13,052 sites (44.8%) and decreased DNA methylation at 16,082 sites (55.2%). Of 29,134 significant CpG sites, 11,850 sites (40.7%) were located in the promoter regions (increased DNA methylation: 39.5%, decreased DNA methylation: 60.5%), 9479 sites (32.5%) in gene bodies (increased DNA methylation: 49.1%, decreased DNA methylation: 50.9%), and 864 sites (3.0%) in 3′-UTRs (increased DNA methylation: 47.5%, decreased DNA methylation: 52.5%). Of 29,134 CpG sites, 7656 sites (26.3%) were located in the CGIs (CpG island) (increased DNA methylation: 33.1%, decreased DNA methylation: 66.9%), 7334 sites (25.2%) in CGI shores (increased DNA methylation: 40.3%, decreased DNA methylation: 59.7%), and 2846 sites (9.8%) in CGI shelves (increased DNA methylation: 55.9%, decreased DNA methylation: 44.1%).