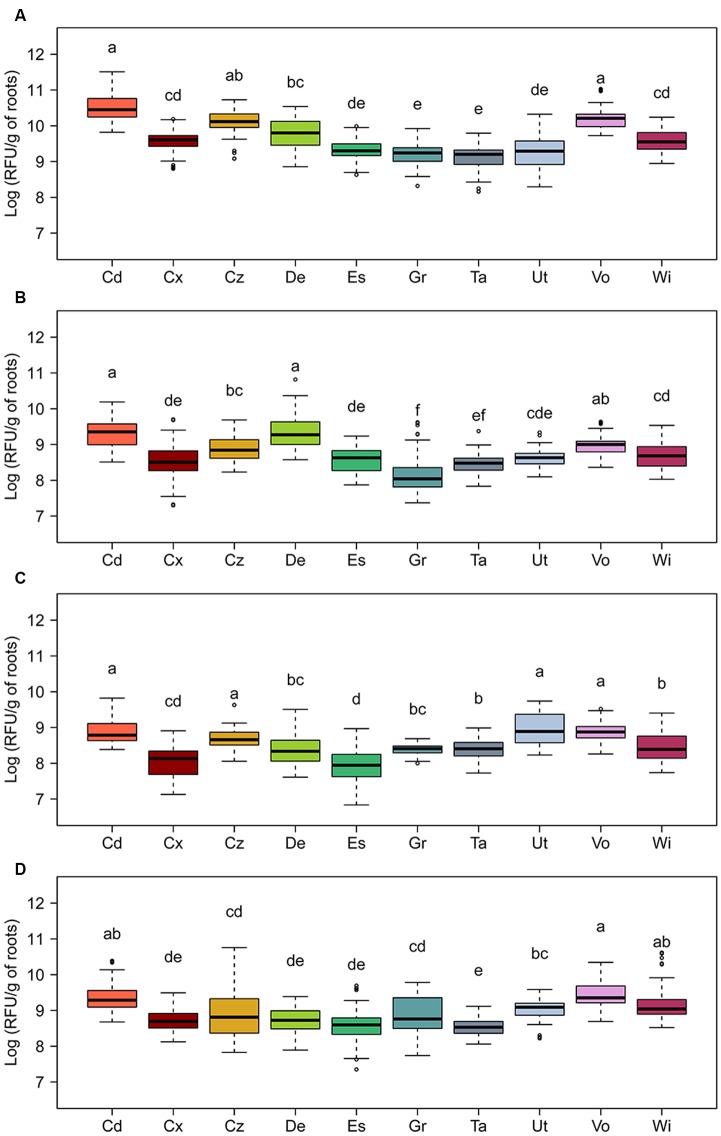
FIGURE 4.
Relative expression of genes required for the biosynthesis of the antimicrobial compounds (A) 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (phlA), (B) hydrogen cyanide (hcnA), (C) pyrrolnitrin (prnA), and (D) phenazines (phzA) on roots of spring wheat in 10 Swiss agricultural soils. Expression was monitored by fluorescence-activated cell-sorting-based flow cytometry using GFP-tagged strains of Pseudomonas protegens (CHA0-gfp) carrying reporter plasmids pME9012 (phlA-mcherry), pME9011 (hcnA-mcherry), or pME11011 (prnA-mcherry) or of P. chlororaphis (PCL1391-gfp) carrying reporter plasmid pME11017 (phzA-mcherry). Seedlings inoculated with the reporter strains were grown in soil microcosms for 5 days prior to analysis of bacterial cells in root washes. Data are shown as relative fluorescence units (RFU) per gram of root dry weight, and were calculated as the median mCherry expression per GFP-tagged Pseudomonas cell multiplied with the total number of GFP-tagged Pseudomonas cells per gram of root. Results from three independent experiments with nine replicates each are presented. Since Kruskal–Wallis analyses did not reveal significant experiment × treatment interactions, data of the three experiments were pooled for statistical analysis. Letters indicate significant differences (Dunn test, p < 0.05). Sampling sites: Cd, Cadenazzo; Cx, Courtedoux; Cz, Cazis; De, Delley; Es, Eschikon; Gr, Grangeneuve; Ta, Taenikon; Ut, Utzenstorf; Vo, Vouvry; Wi, Witzwil.