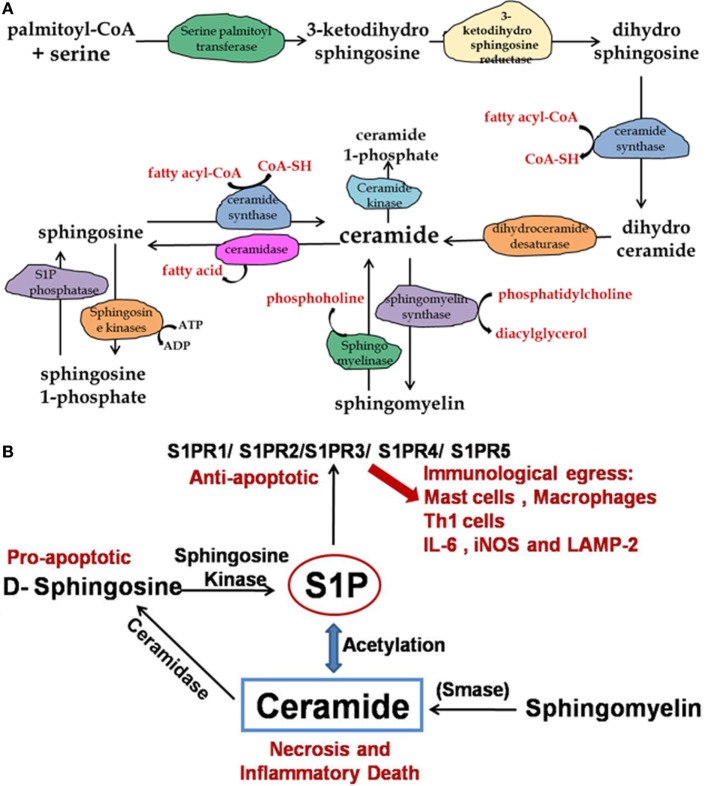
Figure 1.
Pathway for synthesis of ceramide, sphingomyelin, and sphingosine-1 phosphate. (A) The de novo synthesis of ceramide starts with palmitoyl-CoA and serine in endoplasmic reticulum. Ceramide is then converted to sphingomyelin, which is the structural component of outer leaflet of plasma membrane. (B) Enhanced ceramide concentration in lungs results in inflammation and cell damage therefore dynamic balance of sphingosine/S1P/ceramide is important for pathological manifestation during TB infection.