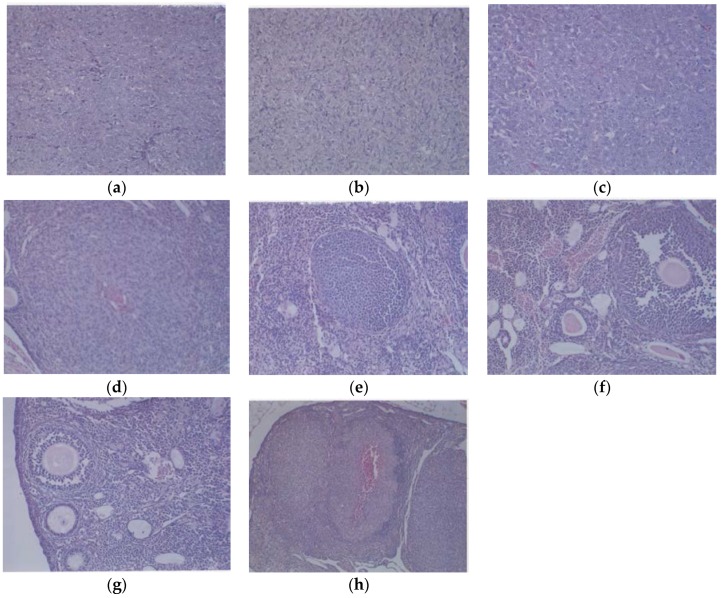
Figure 5.
Histology of representative ovaries in groups: magnification 200× except (h) which is 100×. Control sections shown in (a,b). Sections from EPQ-treated mice shown in (c–h). The representative section shown in (a) presents two sections of a large, round tumor from the Control group which appeared to have destroyed the ovary or ovaries. Necrosis varied from 35% in one section to 65% in the second section. Mitotic figures ranged from 0–1 per high-powered field. The section in (b) shows a large, round mass from the Control group adjoining a small section of the uterus, suggesting it involves an ovary. Cell morphology was similar to (a). Necrosis involved about 50% of the mass. Mitotic figures ranged from 0–1 per high-powered field. The section from the only tumor found in the EPQ group is shown in (c). Sections of uterus, cervix, vagina, and ovaries are seen. Mild to moderate multiple small, glandular cysts are present in the uterus. One ovary was totally replaced by a large tumor composed of irregularly, round cells with indistinct cell borders and irregularly round nuclei. Mitotic figures ranged from 4–5 per high-powered field. Multiple foci of necrosis involved about 40% of the tumor mass. The second ovary has two foci of tumor cells. The section shown in (d) shows a lesion in the second ovary from the same mouse shown in (c) and follicular proliferation is shown in (e). In (e), squamous epithelial hyperplasia is present in the cervix and vagina. Multiple, small, glandular cysts are present in the uterus. No overt tumor is present in the ovary. In (f), a section of uterus, cervix, vagina, and two ovaries shows multiple developing ovaries present in follicles of both ovaries. In (g), representative sections of uterus, cervix, vagina, and two ovaries from mice without ovarian tumors are shown; no significant changes were evident in examined tissues. In (h), a section of uterus, cervix, vagina, and two ovaries, multiple, small glandular cysts are present in the uterus. Both ovaries have 1–4 enlarged luteal or follicular structures, composed of sheets of cells morphologically similar to the neoplastic cells in prior tumors.