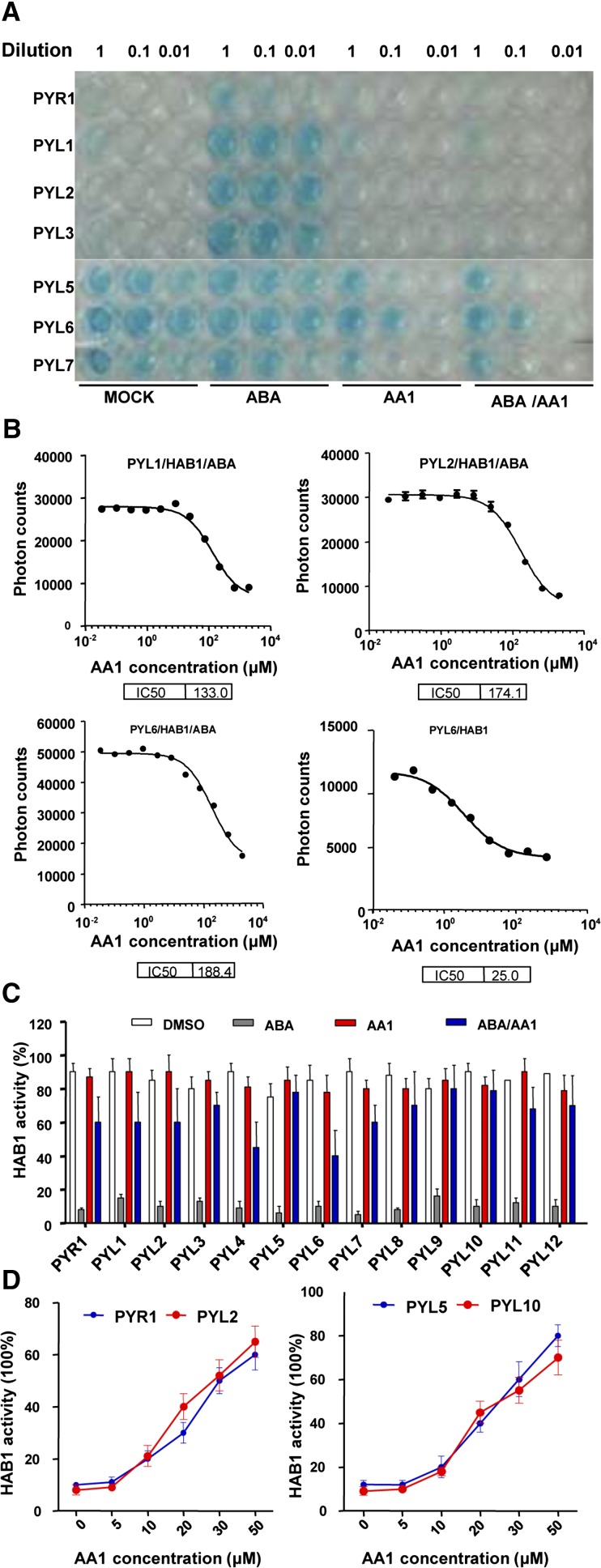
Figure 2.
AA1 interferes with PYR/PYL-PP2C interactions and PYR/PYL-dependent inhibition of PP2C activity. A, AA1 blocks ABA-dependent PYR/PYL-HAB1 interactions in yeast two-hybrid assays. Dimeric receptors (PYR1 and PYL1–PYL3) and monomeric receptors (PYL4–PYL6) were constructed as binding domain fusion proteins; HAB1 was fused with the activation domain. The yeast cells were grown on SD medium (-Leu/-Trp/-His plus 50 mg/L X-α-Gal and 5 mm 3-amino-triazole) with the indicated chemicals for 3 d. Working concentrations of the chemicals were 2 μm for ABA and 100 μm for AA1. The yeast cells were diluted into 1:10 (0.1) and 1:100 (0.01) using water. B, Binding affinity of PYR/PYL proteins to HAB1 measured by AlphaScreen assays. Dimeric receptors (PYL1 and PYL2) and a monomeric receptor (PYL6) were fused with His-SUMO; HAB1 was fused with biotin. The reactions were conducted with and without 100 μm ABA and the indicated concentrations of AA1 (n = 3; error bars = se). IC50, Fifty percent inhibitory concentration. C, AA1 attenuates the ABA-dependent inhibition of HAB1 activity via various ABA receptors. Various PYR/PYL-HAB1 combinations were incubated with the indicated chemicals (2 μm ABA, 100 μm AA1, or DMSO; n = 3; error bars = se). D, Dose-dependent effects of AA1 on PYR/PYL-dependent inhibition of PP2C activity. HAB1 activity was tested with dimeric receptors (PYR1 and PYL2) or monomeric receptors (PYL5 and PYL10) with 2 μm ABA and the indicated concentrations of AA1 (n = 3; error bars = se).