Figure 2.
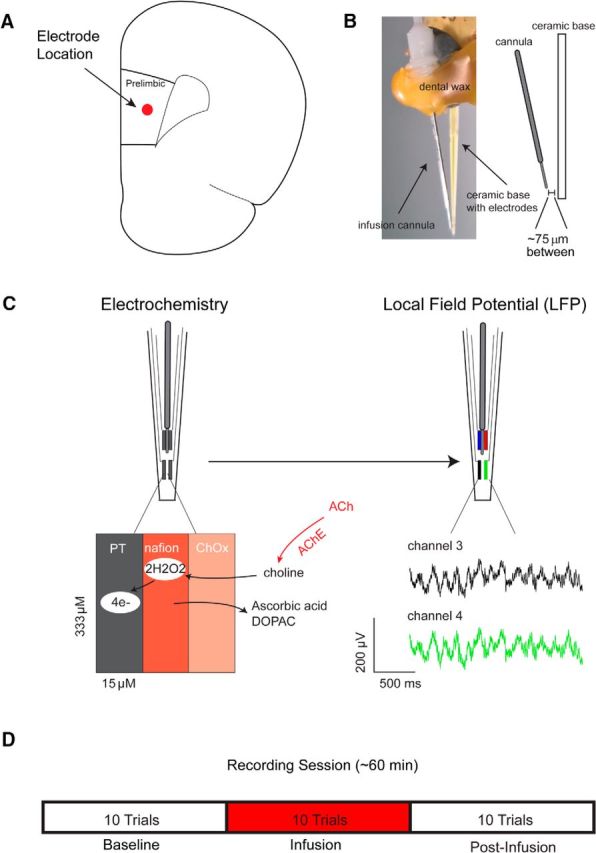
Measurement scheme and experimental design. A, Platinum (PT) microelectrode arrays were implanted into the prelimbic subregion of right prefrontal cortex. B, Local microinfusions were delivered via a cannula connected to the microelectrode array, centered between the four platinum recording sites ∼75 μm from the recording surface. C, Left, For electrochemical recordings, platinum sites were coated with Nafion to control for the contribution of interferents to current signals. Changes in ACh release were measured by converting choline produced by the hydrolysis of newly released ACh to current on the electrode surface. Right, The same electrodes were used to monitor changes in the local field potential in separate sessions. The green and black traces below are representative local field potentials recorded from two electrodes on the same array. D, On drug test days, animals performed 10 baseline trials, followed by 10 trials during which drug (telenzepine, mecamylamine) or vehicle (ACSF) was infused (50 nl/min over 20 min) into the recording area while animals continued to perform the task. During the final 10 trials, no infusion occurred.
