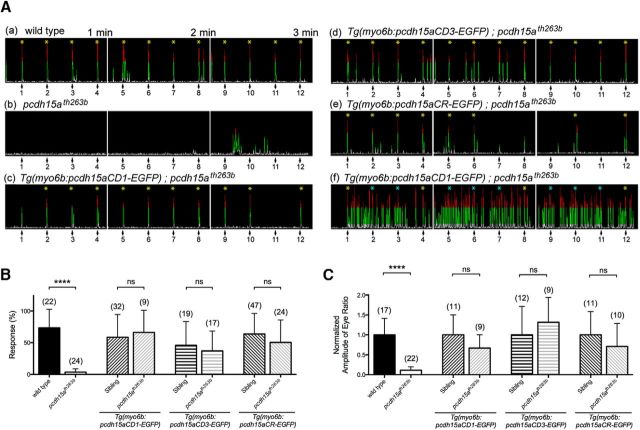
Figure 4.
Rescue of behavioral defects in pcdh15ath263b mutants by either isoform of Pcdh15a. A, Representative time course of the AEBR to a pure tone with 1 kHz at 157 dB at 5 dpf. The stimulus was repeated every 15 s for 3 min. Numbered arrows indicate the stimuli and a yellow asterisk indicates a positive response. The blue asterisks indicate trials that were omitted from the data. The record shown in Aa is an example of a wild-type control larva that responded to every stimulus, Af is a hyperactive larva, Ab is a homozygous mutant larvae, and Ac through Ae are rescue constructs as labeled. B, Startle responses of wild-type, pcdh15a mutant, and rescued pcdh15a mutant larvae at 5 dpf (number of fish is indicated above each bar). The mean and SD is indicated; p-values were determined by unpaired Mann–Whitney U tests, ****p < 0.0001. C, Vestibular-induced eye movements in wild-type, pcdh15a mutant, and rescued pcdh15a mutant larvae at 5 dpf (number of fish is indicated above each bar). The normalized peak amplitude of vestibular-induced eye movements at 0.25 Hz is shown. The mean and SD is indicated; p-values were determined by unpaired Mann–Whitney U tests, ****p < 0.0001.