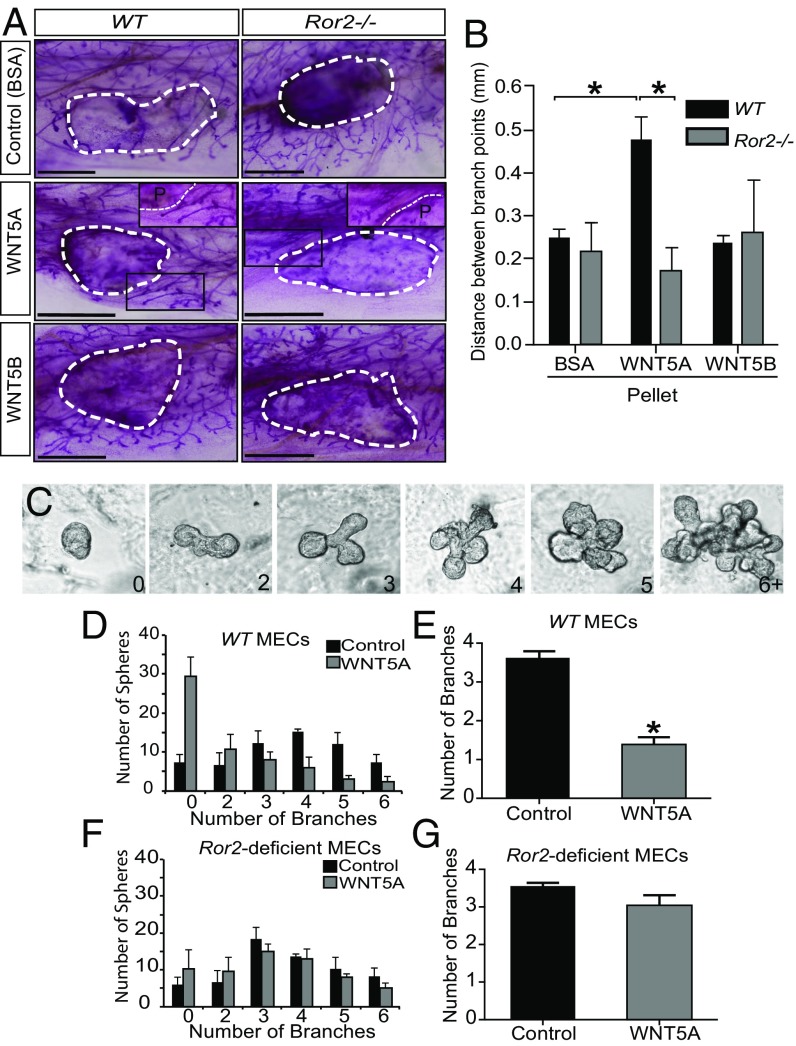
Fig. 3.
WNT5A inhibits mammary branching morphogenesis through ROR2. WT and Ror2−/− fragments were contralaterally transplanted into precleared mammary fat pads. Elvax slow-release pellets containing BSA, WNT5A, or WNT5B were implanted bilaterally 3 wk posttransplant. The tissue was harvested and carmine stained for whole-mount analysis 1.5 wk after the Elvax implantation (A). The distance between branch points was quantified by tracing the ductal structure in proximity of the pellet and measuring the length between branch points (n = 3 lines per five contralaterally transplanted mice per line) (B). Ex vivo branching morphogenesis of reaggregated primary MECs in the presence of FGF2 was carried out over the course of 7 d, and the number of branches per organoid was determined. Example images for organoids with 0–6+ branches are shown (C). WT MECs show significant reduction of organoid branching in the presence of WNT5A compared with control conditions (D and E) (n = 3). Organoids derived from Ror2-deficient MECs show no decrease in the number of branches per organoid when treated with WNT5A (F and G) (n = 3). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. Error bars represent ± SE. (Scale bars, 1.5 mm for A.)