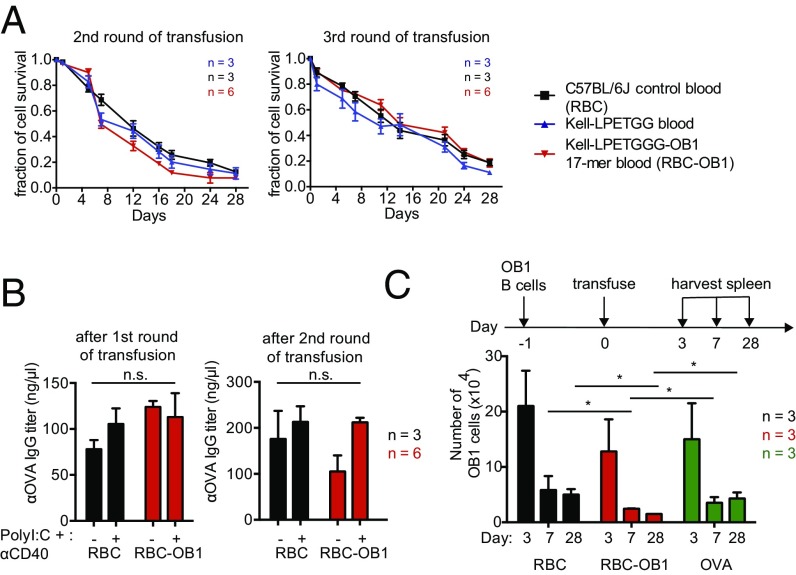
Fig. 2.
OB1 peptide-decorated RBCs blunt responses of OB1-specific B cells. (A) CFSE-labeled RBCs from C57BL/6J and Kell-LPETGG mice were transfused into recipient mice. One set of Kell-LPETGG blood samples were also subjected to sortagging with OB1 peptides before transfusion. Following the first transfusion (as in Fig. 1D), the same cohort is subjected to two more transfusions with a 1-wk gap between each transfusion. RBC survival in the circulation was tracked via CFSE fluorescence by flow cytometry. Repeated transfusions of sortagged RBCs into C57BL/6J mice do not induce faster clearance. (B) A cohort of BALB/c mice was transfused with either C57BL/6J or RBC-OB1. OVA-specific IgG titers at the end of each transfusion were measured by ELISA. (C) Flow cytometry of the total number of adoptively transferred OB1 B cells in spleen, harvested 3, 7, and 28 d after RBC, RBC-OB1, or OVA transfusion. *P < 0.05; ns, not significant.