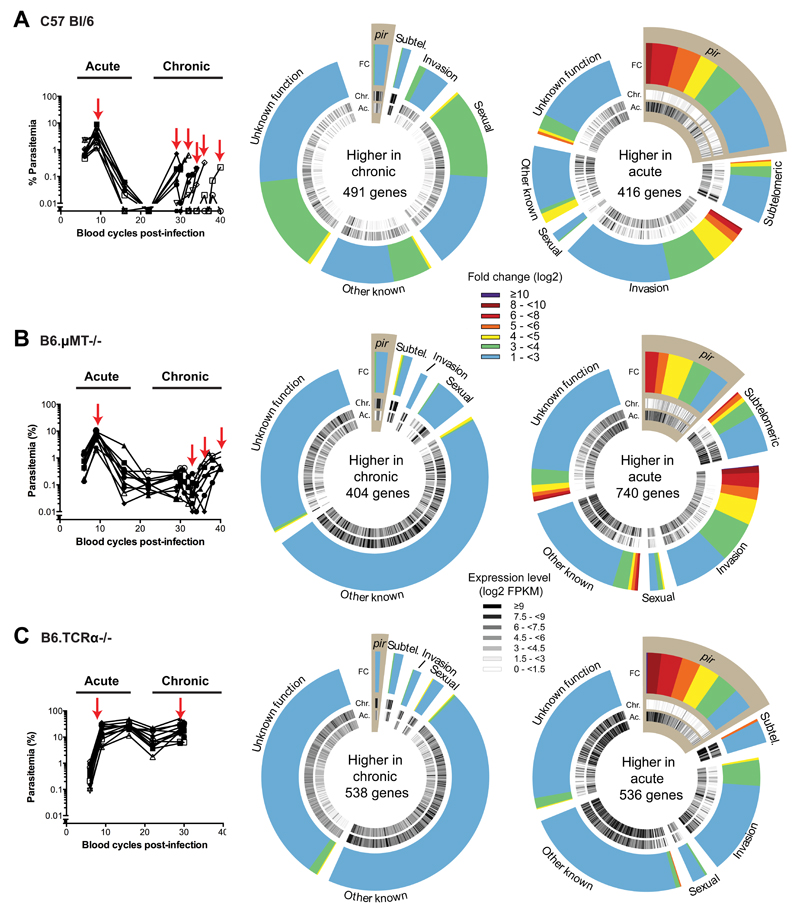
Figure 1. Chronic infections modify the transcriptome of P. chabaudi independently of the adaptive immune response.
Parasitaemias over the course of infection in (A) 10 wild-type C57Bl/6 mice, (B) 10 B6.μMT-/- mice and (C) 10 TCRα-/- mice are shown on the left panels. Parasite mRNAs were collected from 9 wild-type C57Bl/6 mice, 5 B6.μMT-/- mice and 3 TCRα-/- mice selected randomly at the time points indicated by the red arrows. On the right panels, hot pie diagrams show expression levels (black and white inner circles) and fold changes (coloured outer circles) for genes expressed more highly (FDR <= 0.01, fold change >=2) in the chronic and acute phases. Genes are classified into groups according to several categories including: subtelomeric genes (subtel.); genes associated with red blood cell invasion (invasion); genes associated with gametocytogenesis (sexual) and pir genes (highlighted in brown).