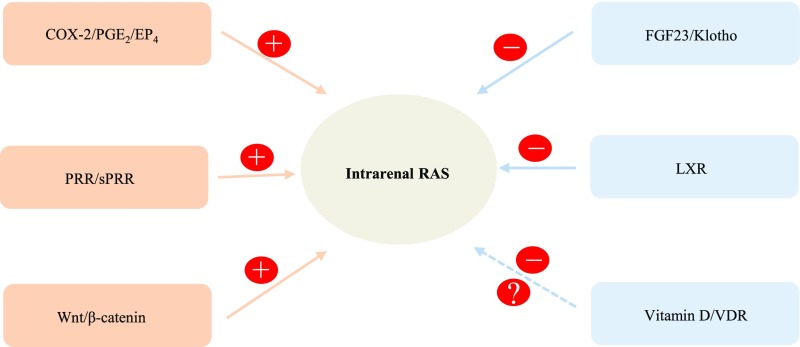
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of regulatory networks that control intrarenal RAS activity. This local system is subjected to tight control by complex regulatory networks consisting of both positive regulators of (pro)renin receptor, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and the PGE2/EP4 pathway, and negative regulators of fibroblast growth factor 23/Klotho, vitamin D/VDR, and LXRs. Imbalance of the two opposing regulatory networks may be an important determinant of intrarenal RAS activity. FGF23, Fibroblast Growth Factor 23; LXR, liver X receptor; VDR, vitamin D receptor.