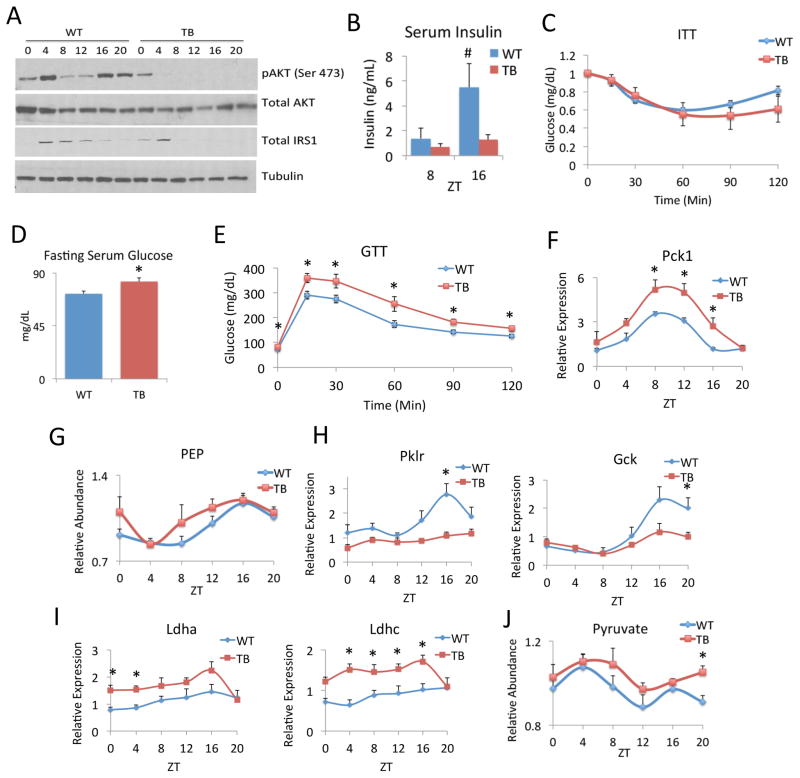
Figure 6. Lung adenocarcinoma alters hepatic insulin signaling and glucose production.
A) Western analysis of phospho-AKT (Ser 473), total AKT and total IRS1 in WT and TB mice over the circadian cycle. B) Serum insulin levels were measured by ELISA at ZT 8 and 16 in WT and TB mouse serum. Insulin levels at ZT 16 are statistically significant as indicated by # (p-value = 0.053, using Student’s T-test). C) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) in WT and TB mice. D) Overnight fasting glucose levels in WT and TB mice. E) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) in overnight fasted WT and TB mice. F) Gluconeogenic gene expression profile of Pepck (Pck1) by RT-PCR was done in livers of WT and TB mice. G) Levels of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) were determined by metabolomics analysis from livers of WT and TB mice. H) RT-PCR of glycolytic gene expression of L-PK (Pklr) and GK (Gck) over the circadian cycle. I) Gene expression of lactate dehydrogenases Ldha and Ldhc in WT and TB mice by RT-PCR. J) Levels of pyruvate were determined by metabolomics in livers of WT and TB mice. Error bars indicate SEM. Significance was calculated using Student’s T test and * indicates a p-value cutoff of 0.05.