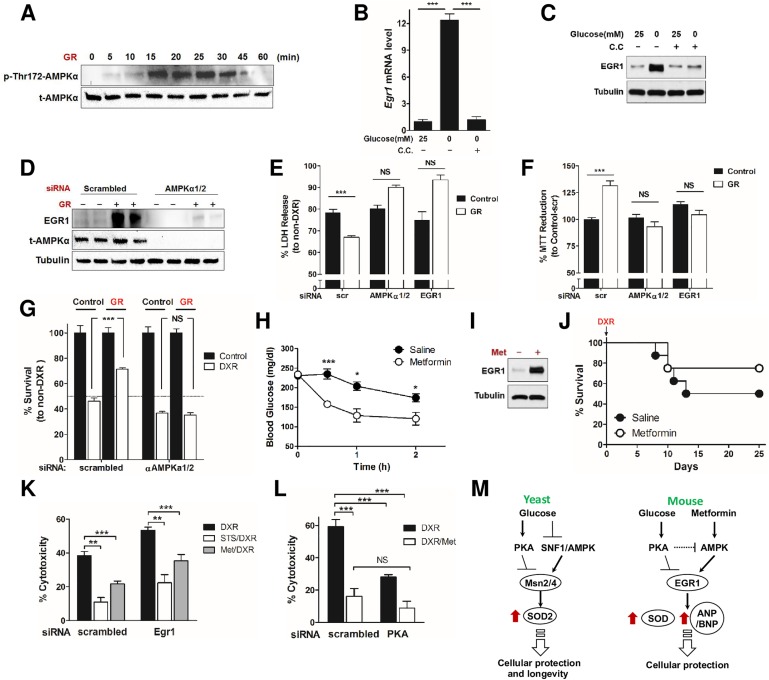
Fig 4. Early growth response protein 1 (EGR1) mediates metformin (Met)-induced stress resistance.
(A) Time-dependent, glucose restriction (GR)-induced AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation was determined by the level of phosphorylation at Thr172 of AMPKα. (B, C) Primary rat cardiomyocytes were pretreated with or without compound C (20 μM) and then incubated with GR or normal medium. Whole-cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by (B) quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and (C) western blotting. (D) H9c2 cardiomyocytes transfected with siRNA against AMPKα1/2 (or a nonspecific control) were treated with GR, and induction of EGR1 was determined by western blotting. (E, F) H9c2 cardiomyocytes were treated with siRNA against AMPKα1/2 or Egr1 or a nonspecific control and treated with doxorubicin (DXR). Cytotoxicity was determined by (E) % LDH release compared to corresponding non-DXR treated groups and (F) % 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction compared to the group treated with nonspecific control siRNA not treated with DXR (n = 8). (G) H9c2 cardiomyocytes were treated with siRNA against AMPKα1/2 or a nonspecific control and treated with and without GR and DXR. % survival was determined by trypan blue exclusion and normalized to each non-DXR treated group (n = 5–6). (H) Blood glucose levels from Met- and saline-injected mice were monitored for 2 h. (I) Primary rat cardiomyocytes were treated with Met (20 mM), and the expression level of EGR1 was analyzed by immunoblot. (J) Met-induced stress resistance. C57BL6 mice were injected daily with Met (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneal [IP]) for 2 wk prior to DXR administration (24 mg/kg). Survival was monitored for 25 d (n = 11; not statistically significant). (K) Cardiomyocytes transfected with siRNA against PKA were treated with Met (20 mM) and 24 h later were treated with DXR (1 μM). Cytotoxicity was measured 24 h after DXR treatment by LDH release to assess cell viability. (L) Cardiomyocytes transfected with siRNA against PKA (or a nonspecific control), were treated with Met (20 mM) and 24 h later were treated with DXR (1 μM). Cytotoxicity was measured 24 h after DXR treatment to assess cell viability. (M) A model for the starvation and/or Met-mediated AMPK/PKA-EGR1 (Msn2/4) pathways in yeast and mice. Both starvation (glucose restriction) and Met (Met in mice only) activate AMPK and inhibit protein kinase A (PKA), converging on Egr1 induction (Msn2/4 in yeast). In agreement with other studies [36–38], PKA may negatively regulate AMPK. The consequent induction of Egr1 or Msn2/4 triggers the expression of antioxidants, stress response genes (in both yeast and mice), and cardiac peptide hormones ANP/BNP, eventually enhancing cardioprotection (in mice). Technical replicates for the in vitro experiments are reported in B, E–G, K, and L (n = 3 to 4), and data are represented as mean ± SEM. The significance of the differences between experimental groups was determined by using one-way ANOVA (Tukey post-analysis test). Comparisons between groups were performed with Student’s t test. p-value < 0.05 were considered significant (p-value < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001 are indicated as *, *, and ***, respectively). Underlying data and method of statistical analysis are provided in S1 Data.