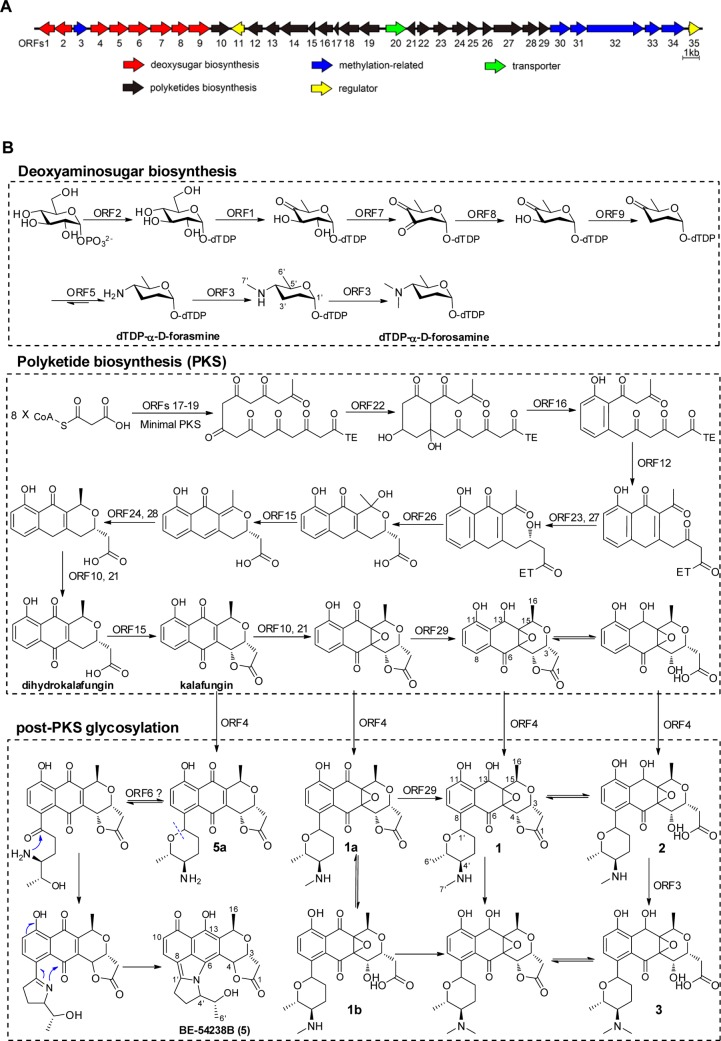
Figure 3.
Biosynthetic pathway of qinimycins and BE-54238A/B. (A) Organization of the qin locus in Streptomyces sp. MBT76. For annotation of the respective gene products see Table 1. Genes for the minimal PKS (presented in black) are similar to those for biosynthesis of the pyranonaphthoquinone kalafungin, while the eight genes in red encode enzymes for production of deoxyaminosugar d-forosamine. (B) Proposed biosynthetic route to qinimycins. The exact function of each gene was assigned in every specific biosynthesis step. The intriguing feature for qinimycins biosynthesis is reduction of the C-13 ketone probably catalyzed by qin-ORF29, while the pyrrole ring in the antibiotics BE-54328A/B originated from the six-membered deoxyaminosugar forosamine.