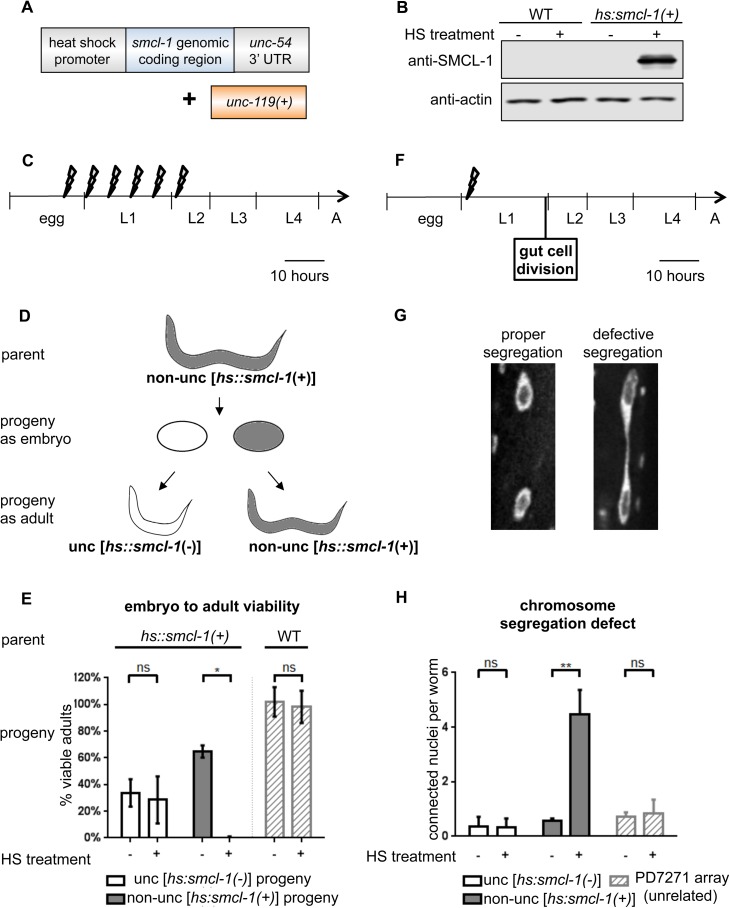
Fig 5. SMCL-1 overexpression leads to lethality and chromosome segregation defects.
(A) The conditional overexpression transgene. The smcl-1 genomic sequence is driven by the hsp-16.48 promoter and contains the unc-54 3’UTR. The transgene was co-injected with unc-119(+) as the positive selection marker into unc-119(ed9) mutant worms. Worms containing multicopy transgene arrays with both the overexpression transgene and positive selection marker are designated hs:smcl-1(+). (B) Western blot of standard lysate showing increase in SMCL-1 protein level after heat shock in hs:smcl-1(+) worms, compared to an actin control. (C) Heat shock regimen for data in (E). Bolt symbols represent heat-shock pulses administered from late embryo to early L2 larval stage. (D) Cartoon explaining segregation of the extrachromosomal transgene array. Parents that are hs:smcl-1(+) give rise to embryos without the overexpression array indicated hs:smcl-1(-), and with the overexpression array indicated hs:smcl-1(+) and shaded gray; upon hatching, the progeny are identified by their uncoordinated and non-uncoordinated movements, respectively. Mosaics are also produced (not depicted). (E) Viability of progeny from hs:smcl-1(+) or wild-type (WT) parent worms after no heat shock (-, bottom) or after heat-shock pulses (+, bottom). For hs:smcl-1(+) parents, y-axis represents percent of embryos that develop into uncoordinated hs:smcl-1(-) adults without the transgene (white bars) or into non-uncoordinated hs:smcl-1(+) adults with the transgene (gray bars). Note no transgene-expressing progeny survive heat shock-induced smcl-1 overexpression. For wild-type parents, y-axis represents percent of embryos that develop to adults (striped bars). (F) Heat shock regimen for data in (H). Bolt symbol represents a single 2-hour heat-shock pulse administered at early L1 larval stage to monitor effects of smcl-1 overexpression on nuclear divisions in the gut that occur at late L1 larval stage. (G) Adult gut cells with DNA stained by DAPI and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Connected chromatin between nuclei (right) indicates a prior chromosome segregation defect. (H) Chromosome segregation defect in the gut. L1 progeny of transgenic hermaphrodites were subjected to heat shock (+, bottom) or no heat shock (-, bottom) Some L1s were uncoordinated hs:smcl-1(-) L1 larvae without the transgene (white bars); others were non-uncoordinated hs:smcl-1(+) with the smcl-1 overexpression transgene (gray bars). The number of connected nuclei per worm, which indicates defective chromosome segregation, was scored in >40 worms of each genotype. PD7271 is a control strain that contains an unrelated extrachromosomal array. HS = heat shock. ** denotes p ≤ 0.01; * denotes p ≤0.05; ns = not significant by a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test. Bars represent 95% confidence intervals.