Figure 1. PD-1−/− mice produce increased dBSM- and Tn+ tumor mucin-specific Ab following dBSM and Qβ-Tn immunization.
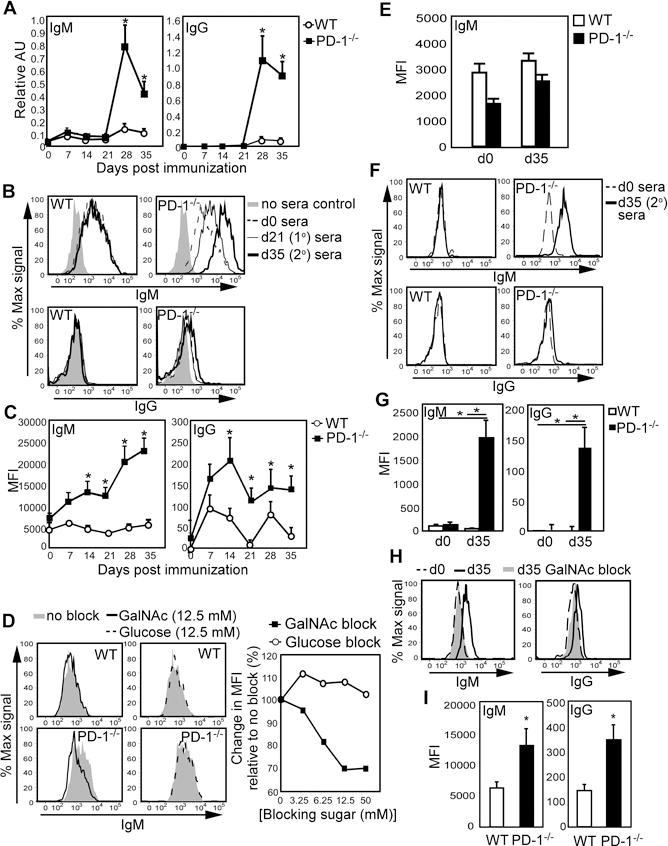
A–H) WT and PD-1−/− mice were immunized with 100μg dBSM on d0 and 21. A) Mean(± SEM) dBSM-specific serum IgM and IgG concentrations. B–C) Serum IgM and IgG reactivity with TA3-Ha cells. Representative staining (B) and average MFI (±SEM) values (C). Results representative of 4 independent experiments. D) GalNAc but not glucose inhibits IgM from dBSM-immunized PD-1−/− mice (d28) from binding TA3-Ha cells. E) Serum IgM (mean MFI ±SEM) reactivity with E0771 cells. F–H) Immune (d35; n=7–8 mice/group) and naive serum IgM and IgG reactivity with Jurkat cells. Representative staining (F) and mean MFI (±SEM) values (G). H) GalNAc(50 mM) inhibits PD-1−/− serum (d35) from binding to Jurkat cells. I) Mice were immunized with 5 μg Qβ-Tn on d0 and d21. Serum IgM reactivity (d35) with TA3-Ha cells shown as mean MFI(±SEM; n≥6/group). Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences (p <0.05) between mean values.
