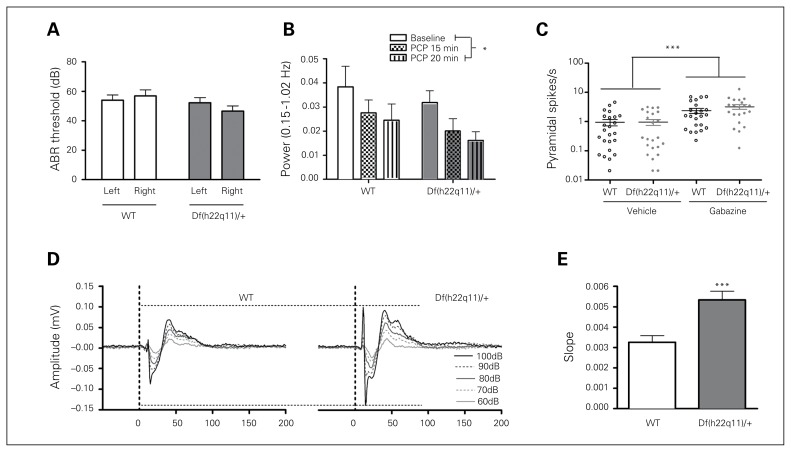
Fig. 4.
Electrophysiological measures in Df(h22q11)/+ and wild-type (WT) littermates. (A) Hearing did not differ between the Df(h22q11)/+ mice and WT littermates (n = 13/group, 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA, genotype: F1,24 = 1.649, p = 0.211; ear: F1,24 = 0.331, p = 0.571; ear × genotype: F1,24 = 3.570, p = 0.071). (B) Phencyclidine (PCP) caused similar decrease of cortical low-frequency oscillations (LFOs) in WT and Df(h22q11)/+ mice (n = 9/group, 2-way ANOVA, genotype: F1,48 = 2.40, p = 0.13; condition: F2,48 = 3.44, p = 0.040; genotype × condition: F2,24 = 0.013, p = 0.99). (C) Gabazine caused a similar increase in pyramidal spike frequencies in WT and Df(h22q11)/+ mice (n = 14/group, 2-way ANOVA; genotype: F1,87 = 1.21, p = 0.28; treatment: F1,87 = 20.9, p < 0.001; genotype × treatment: F1,87 = 1.12, p = 0.29). (D) Grand average loudness-dependent auditory evoked potentials (LDAEP) waveforms from the auditory cortex (AuC) in WT and Df(h22q11)/+ mice (n = 22–23/ group, 2-way repeated-measure ANOVA, P1/N1 genotype: F1,43 = 22.6, p < 0.001; intensity: F4,43 = 75.5, p < 0.001; genotype × intensity: F4,43 = 13.7, p < 0.001; N1/P2 genotype: F1,43 = 9.89, p = 0.003; intensity: F4,43 = 156.4, p < 0.001; genotype × intensity: F4,43 = 9.76, p < 0.001). (E) Collapsed LDAEP slopes for Df(h22q11)/+ and WT mice (n = 22–23/group, t test; t43 = −3.896, p < 0.001). Data are presented as means ± standard errors of the mean. *Significant differences (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001). ABR = auditory-induced brainstem response.