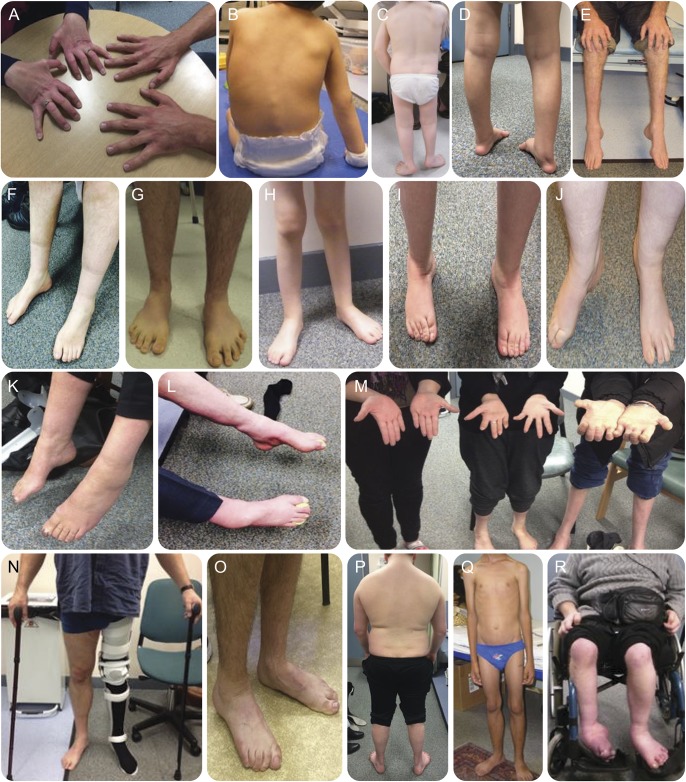
Figure 1. Clinical heterogeneity of different forms of hereditary motor neuropathy (HMN).
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy (dHMN) (top 2 rows), motor Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 2 (CMT2) (third row), and HMN plus (bottom row): (A) patients 2 and 3: GARS; (B) patient 19: IGHMBP2; (C) patient 23: TRPV4; (D) patient 32: IGHMBP2; (E) not yet diagnosed dHMN; (F) patient 18: DYNC1H1; (G) patient 10: SYT2; (H) patient 16: BICD2; (I, J) not yet diagnosed spinal muscular atrophy lower extremity dominance; (K) patient 42: AARS; (L) patient 39: AARS; (M) family 22: DNM2; (N) patient 51: FUS; (O) patient 53: ATP7A; (P) patient 57: TBX5; (Q) patient 58: STAT5B; (R) not yet diagnosed HMN plus.