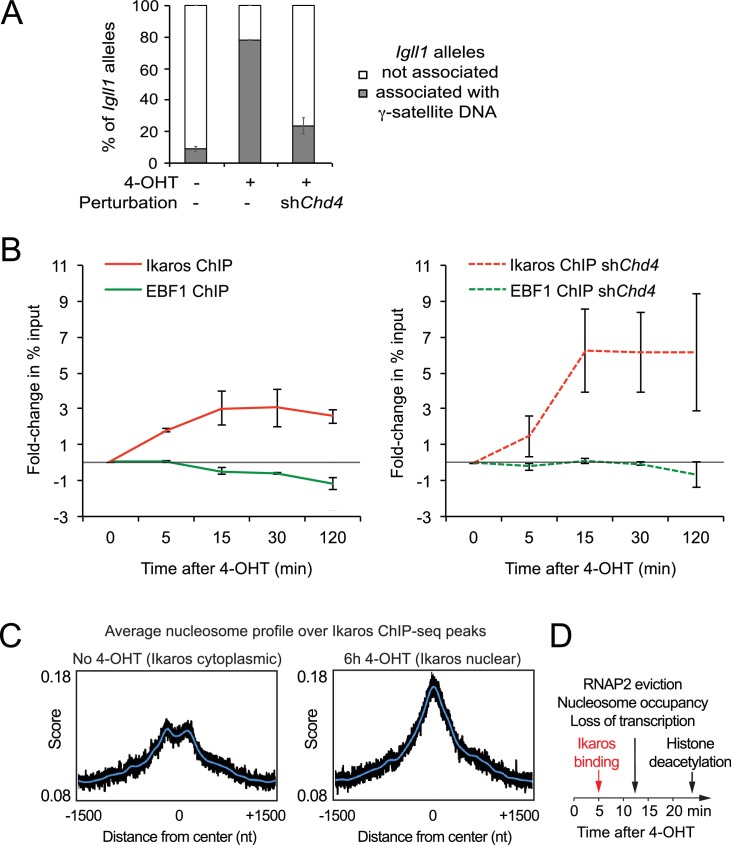
Figure 7. Interdependence of silencing mechanisms leveraged by Ikaros.
(A) 3D DNA-FISH to monitor the position of Igll1 alleles (green) relative to γ-satellite DNA (red, blue is DAPI). The percentage of Igll1 alleles associated with γ-satellite DNA is shown as mean ± SE. Where indicated, control or shChd4 cells were treated over night with 4-OHT. At least 300 Igll1 alleles were scored for each experimental condition across 3 independent biological replicates. The impact of Chd4 knockdown was statistically significant across replicates (p=5.54×10-38 GLM binomial logit). (B) ChIP kinetics of Ikaros and EBF binding to the Igll1 promoter in control (left) and shChd4 cells (right). Increased binding of Ikaros to the Igll1 promoter was significant for both control and shChd4 cells, decreased binding of EBF1 was significant in control, but not in shChd4 cells. Mean ± SE, 3 independent biological replicates. Ikaros and EBF1 binding at 15, 30 and 120 min were significantly higher in shChd4 than control cells. (C) MNase-seq data from 3 independent biological replicates were integrated with Ikaros ChIP-seq data to show nucleosome occupancy at Ikaros binding peaks before and 6 hr after nuclear translocation of Ikaros. (D) Dynamics of Ikaros binding, RNAP2 eviction, loss of primary transcripts, nucleosome invasion, and histone deacetylation.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22767.023