Fig. 1. Stroke Induced Motor Impairment.
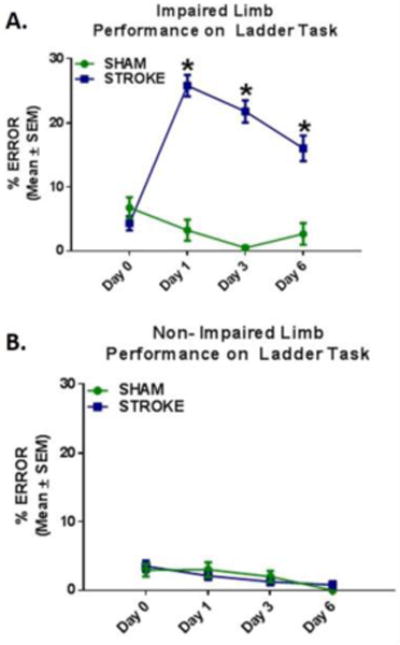
(a) Following injury, animals made significantly more errors with their impaired limb compared to sham controls. (b) There was no difference in errors made with the non-impaired forelimb between stroke and sham animals. Values reported as mean ± SEM. n ≥ 10, *p < 0.005
