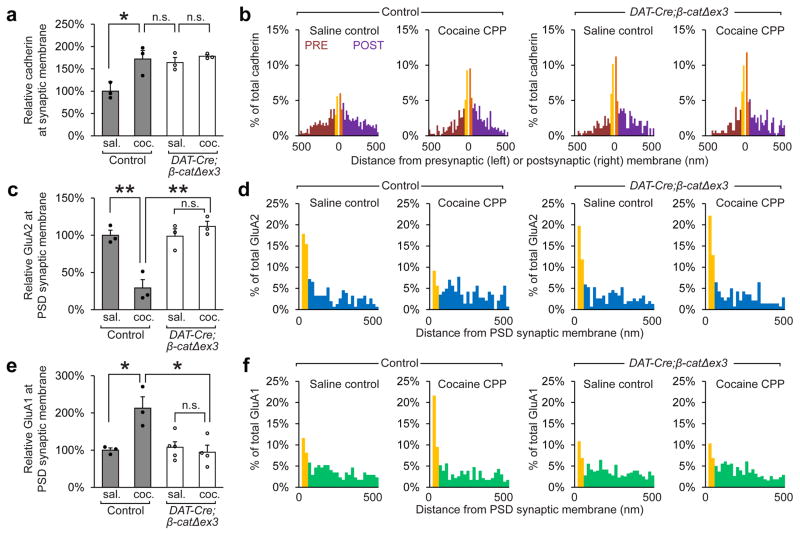
Figure 4. Stabilization of cadherin at synapses in the VTA prevents the removal of GluA2-containing AMPARs, and blocks the insertion of GluA1-containing AMPARs.
Immunogold EM was used to identify differences in cadherin, GluA2, and GluA1 localization after cocaine CPP in wildtype and DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3. (a, b) Cadherin localization to the synaptic membrane was increased under basal conditions in DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3 mice, and recruitment of additional cadherin to the synaptic membrane during CPP was blocked (p<0.05, significant interaction between treatment and genotype, two-way ANOVA, F(1,8) = 5.613, n=3 mice per condition. >100 synapses were analyzed per group). (c, d) The removal of GluA2 from the PSD membrane at excitatory synapses following CPP was blocked in DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3 mice (p<0.01, significant interaction between treatment and genotype, two-way ANOVA, F(1,8) = 22.07, n=3 mice per condition). (e, f) The insertion of GluA1 to the PSD membrane at excitatory synapses onto dopaminergic neurons following CPP was blocked in DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3 mice (p<0.01, significant interaction between treatment and genotype, two-way ANOVA, F(1,11) = 10.75, n=3 mice control saline, n=3 mice control cocaine; n=5 DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3 mice saline, 4 DAT-Cre;β-catΔex3 mice cocaine). a, c, e: *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01 Bonferroni’s test post hoc. Data shown as mean ± SEM with individual mice (circles) overlaid.