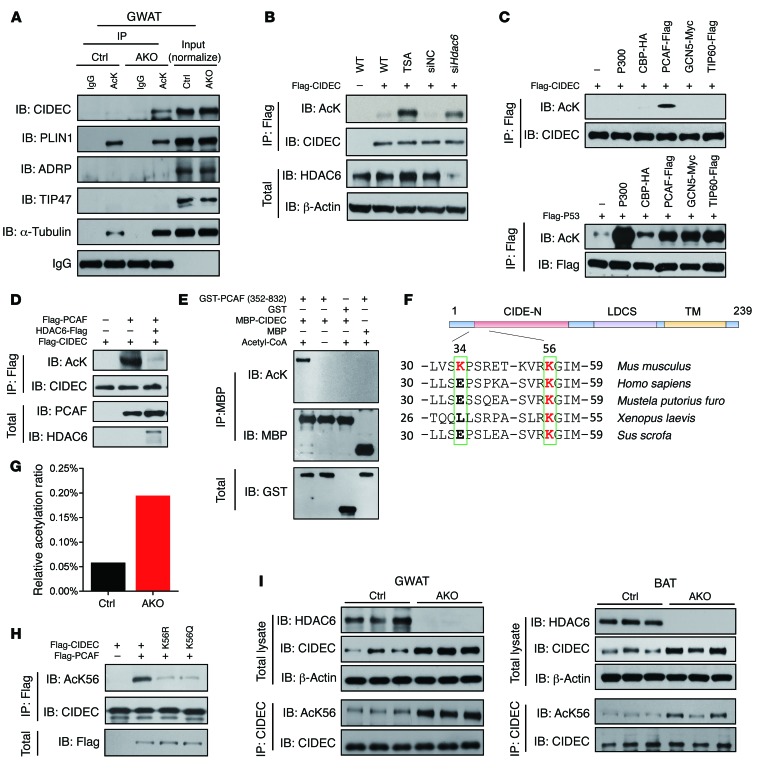
Figure 3. CIDEC is deacetylated by HDAC6 and acetylated by PCAF at K56.
(A) Levels of CIDEC acetylation were increased in the GWAT of Hdac6 AKO mice. Levels of α-tubulin were used as a positive control. IgG was used as a loading control. To detect CIDEC acetylation in vivo, the GWAT tissue sample was incubated with A/G beads conjugated to antibodies against acetylated lysine, and the immunoprecipitates were blotted with antibodies against CIDEC and other LD-associated proteins (PLIN1, ADRP, TIP47). Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (B) Ectopically expressed CIDEC was acetylated in the presence of TSA or when Hdac6 was knocked down. Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (C) PCAF acetylates CIDEC. Flag-CIDEC was coexpressed in 293T cells with different acetyltransferases. Upper panel shows levels of CIDEC acetylation; lower panel shows levels of P53 acetylation when Flag-CIDEC and Flag-P53 were coexpressed with various acetyltransferases. Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (D) HDAC6 deacetylates CIDEC. Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (E) PCAF acetylates CIDEC in vitro. Bacterially isolated CIDEC-MBP was incubated with GST-PCAF containing the enzymatic domain (active) in vitro. Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (F) Identification of the conserved K56 residue in difference species. (G) Ratio of acetylated CIDEC at K56 in the adipose tissue of control and Hdac6 AKO mice. (H) Characterization of anti–acetyl-K56 (AcK56) antibody. Data represent results from at least 3 independent experiments. (I) Increased levels of CIDEC protein and its acetylated form in the GWAT and the BAT of Hdac6 AKO mice. The immunoprecipitated CIDEC was normalized (n = 3 mice per group).