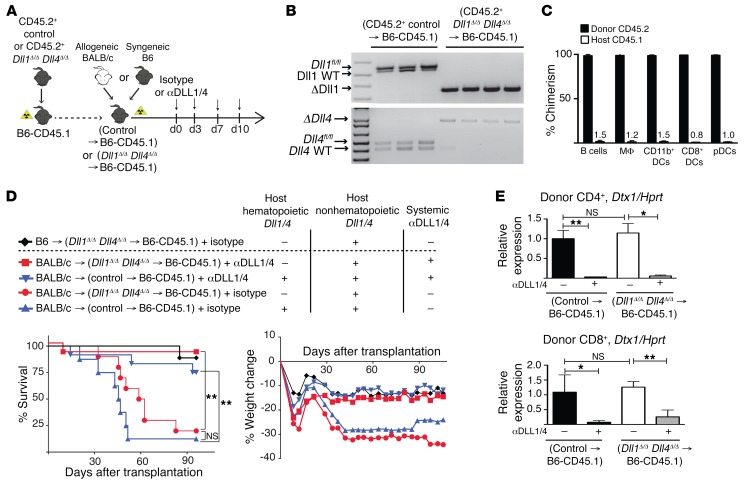
Figure 2. Host hematopoietic cells are dispensable as cellular sources of DLL1/4 Notch ligands in acute GVHD.
(A) Experimental strategy. BM chimeras were generated via transplantation of syngeneic B6-CD45.2+ poly(I:C)-induced TgMx1-Cre– littermate control or TgMx1-Cre+ Dll1Δ/Δ Dll4Δ/Δ BM into irradiated B6-CD45.1 recipients. After reestablishment of steady-state hematopoiesis 12 weeks later, BM chimeras were subjected to a second syngeneic or allogeneic transplant, with or without systemic anti-DLL1/4 blockade. (B) Quantification of Dll1 and Dll4 inactivation in sort-purified Gr1+CD11b+ blood myeloid cells from BM chimeras 12 weeks after transplantation (PCR). In this particular experiment, control BM chimeras were generated from poly(I:C)-induced TgMx1-Cre– Dll1fl/+ Dll4fl/+ donor mice. Each lane represents an individual mouse. (C) Donor chimerism (frequency of CD45.2+ donor cells) in the indicated splenic cell populations 12 weeks after transplantation. MΦ, macrophages; pDCs, plasmacytoid DCs. (D) Survival and weight loss of lethally irradiated (11 Gy) BM chimeras transplanted with 8 × 106 TCD BM plus 30 × 106 B6 splenocytes (syngeneic control) or 30 × 106 allogeneic BALB/c splenocytes (allo-BMT). Isotype control or anti-DLL1/4 antibodies were injected i.p. on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 (n = 10 mice/group). (E) Abundance of Dtx1 Notch target gene transcripts (qRT-PCR) in sort-purified donor CD4+ T cells and CD8+ cells on day 6 (n = 5 mice/group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and NS = P > 0.05, by unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test with Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons. Data are representative of at least 2 experiments; error bars indicate SD.