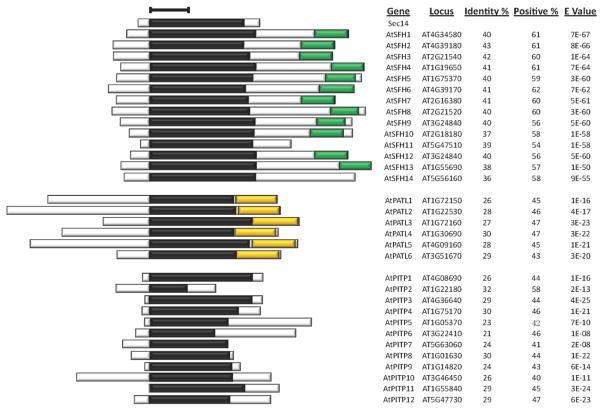
Figure 1. Arabidopsis Sec14-homology proteins.
Sec14-like proteins were identified by interrogating NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), greenphyl (http://www.greenphyl.org/cgi-bin/index.cgi), and phytozome (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html) databases with yeast Sec14 as query primary sequence and BlastP as search tool using default parameters (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome). For confirmed the Sec14-homology proteins, the nodulin domain was further screened using Nlj16 sequence as query primary sequence and BlastP as the search tool with default parameters. A hit score of 40 was set as the BlastP cutoff value. The GOLD domain was scanned by the InterPro tool (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search) with default parameters. Sec14 domains are indicated by black boxes; nodulin domains are in green, and GOLD domains are in gold. Bar = 100 amino acids. Gene designations and locus identifiers, primary sequence identities and positive similarities of corresponding Sec14-domains to yeast Sec14, and corresponding E-values are listed at right.