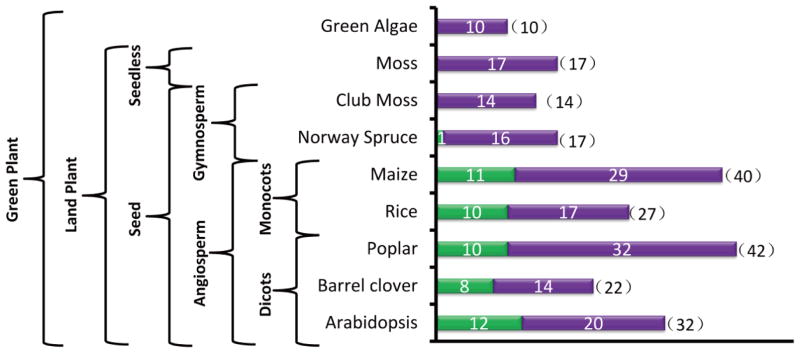
Figure 3. A survey of Sec14-nodulin proteins across the plant kingdom.
BlastP searches using the yeast Sec14 as query primary sequence against NCBI: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, greenphyl: http://www.greenphyl.org/cgi-bin/index.cgi, and phytozome: https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html databases were performed. For confirmed the Sec14-homology proteins, the nodulin domain was further screened using Nlj16 sequence as query primary sequence and BlastP as the search tool with default parameters. A hit score of 40 was set as the BlastP cutoff value. Indicated plant species were analyzed. Numbers of total Sec14-like proteins and Sec14-nodulin proteins are plotted. Green bars indicate numbers of Sec14-nodulin proteins, and purple bars indicate numbers of Sec14-like polypeptides without nodulin domains. Numbers in parentheses indicate total Sec14-like proteins produced by the indicated plant species. Taxonomic hierarchy of the selected plant species surveyed is shown at left.