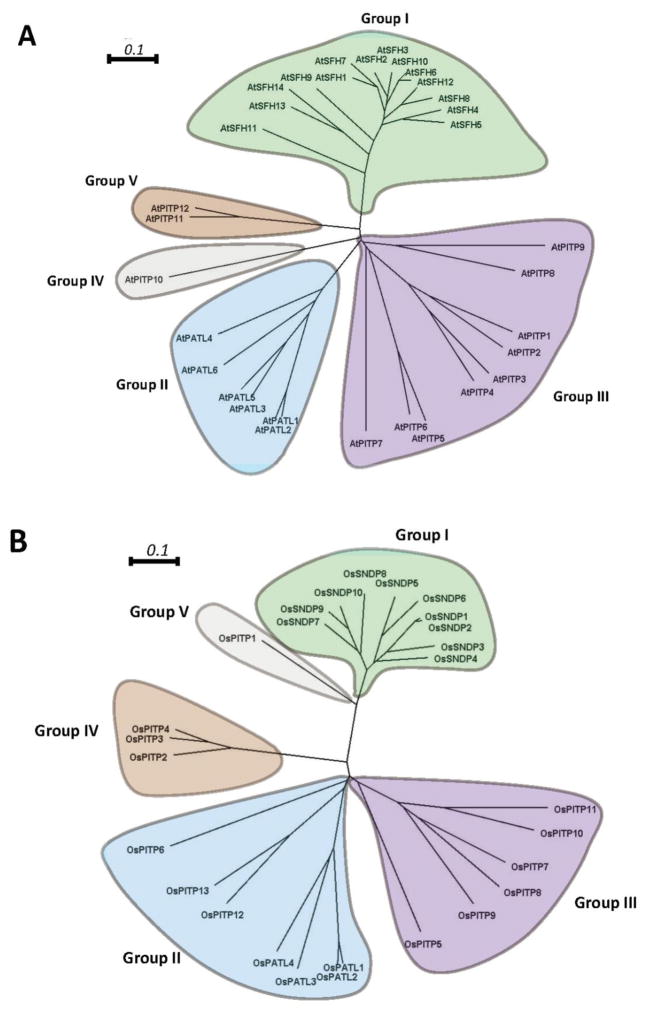
Figure 4. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Arabidopsis and rice Sec14-like domains by the neighbor-joining method.
Arabidopsis (A) and rice (B) Sec14-domain primary sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/) with the default parameters except order = input. Aligned sequence files were the process using the ClustalW2 phylogeny tool with default parameters (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/phylogeny/clustalw2_phylogeny/). The phylogenetic tree files were plotted and edited using SplitsTree4. For both the Arabidopsis and the rice analyses, the Sec14-domains were classified into 5 clades. These clades are designated Group I - Group V and are highlighted by differential coloring. Bars = 0.1 represent amino acid genetic changes of 0.1 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/phylogeny/clustalw2_phylogeny/).