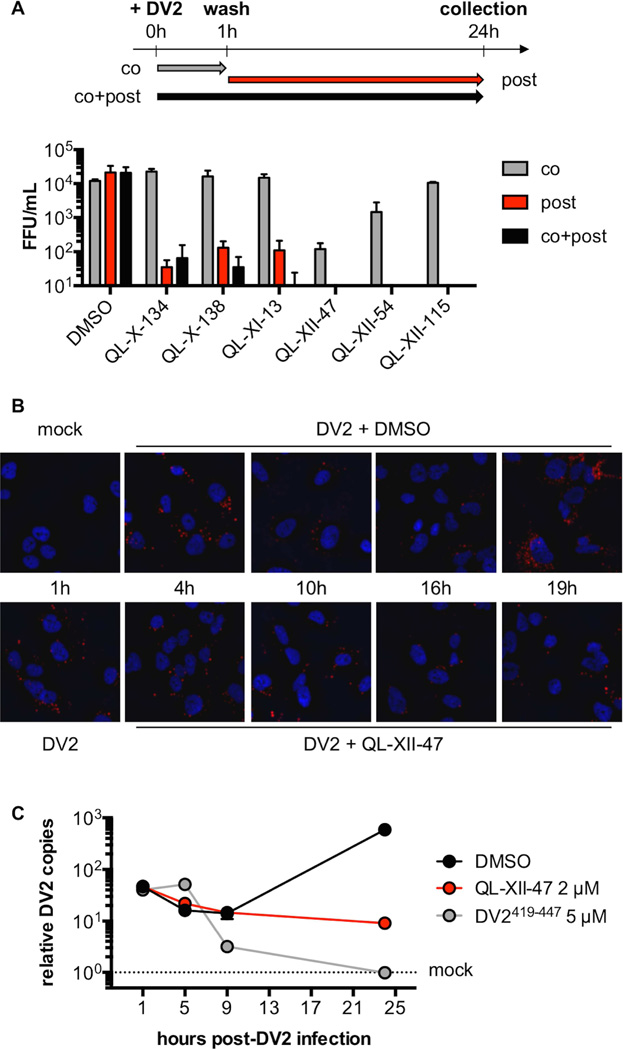
Figure 2. QL-XII-47 and related quinolines do not affect viral entry.
A. In time-of-addition studies, Huh7 cells were infected with DV2 at MOI of 1. The cells were treated with 2 µM of small molecules concomitant with the infection (co), post-infection (post), or at both times (co+post). The infectious virus released to the supernatants at 24 hours post-infection was quantified by FFA. Representative data (mean ±standard deviation of experimental duplicates) out of n=2 independent experiments are shown.
B. To monitor the DV2 genomic RNA, Huh7 cells were mock-infected, or infected with DV2 at a MOI of 10 for 1 hour and then treated with DMSO or 2 µM of QL-XII-47. Cover slips were collected at the indicated times post-infection, and DV2 RNA was detected by in situ hybridization assays (in red). Nuclei were stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, in blue). Representative images taken at 400x magnification from one of n>3 independent experiments are shown.
C. To quantify the abundance of intracellular DV2 RNA, Huh7 cells were mock- infected, infected with DV2 at a MOI of 1 for 1 hour and then were treated with DMSO or 2 µM of QL-XII-47. Control cells were infected with DV2 that had been pretreated with DV2419-447 (5 µM, 37°C, 15 min). Total RNA was collected at the indicated times post-infection, and DV2 RNA was quantified by RT-qPCR. The results were normalized to GAPDH mRNA and are expressed as fold increase over mock-infected controls. Representative data (mean ±standard deviation of experimental duplicates) out of n=2 independent experiments are shown.