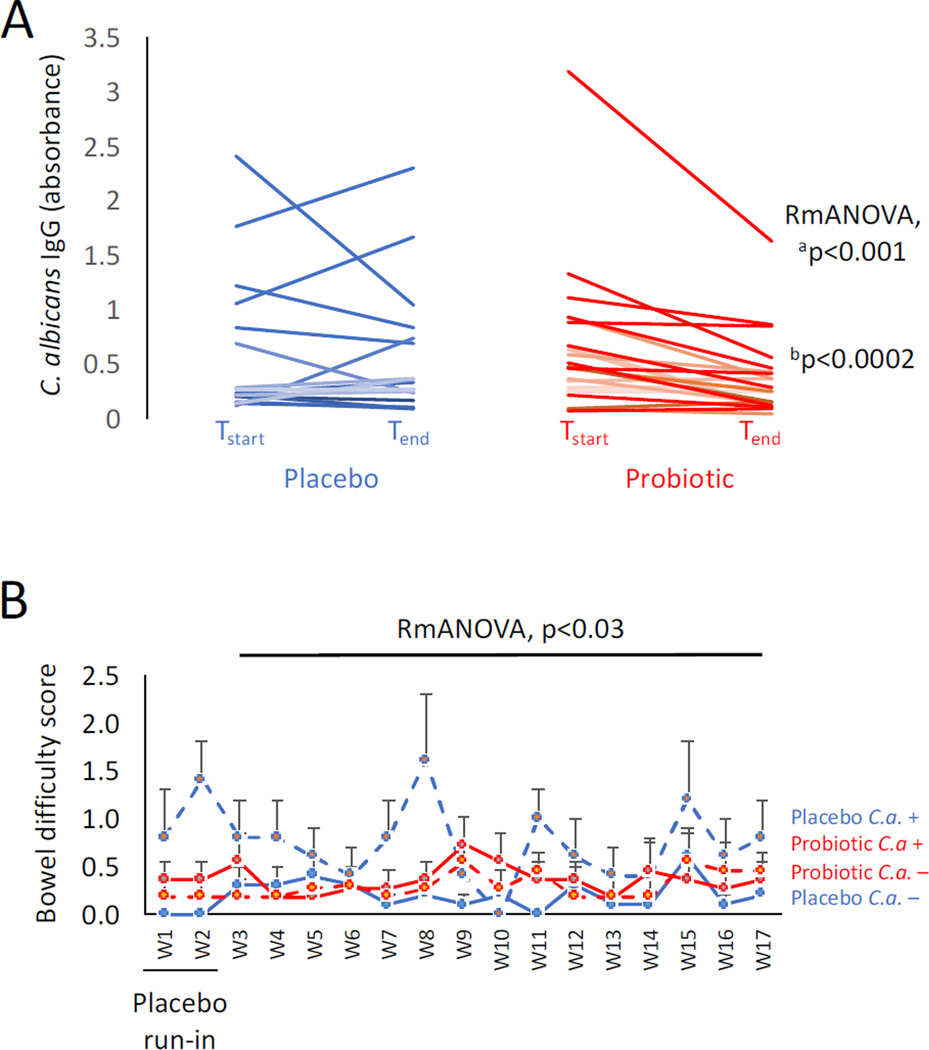
Figure 1. Reduction of C. albicans IgG antibodies and improvement of bowel difficulty in males receiving probiotics.
Panel A: Males with schizophrenia had significantly lower C. albicans antibody levels following a 14-week regimen of probiotics (n=22) compared to those receiving placebo (n=15). Tstart refers to study start and Tend refers to study end. Repeated measures ANOVA (RmANOVA) showed significantly reduced antibody levels associated with the probiotic treatment group over time. ap≤0.001 refers to the p-value including all individuals; bp≤0.0002 refers to the p-value with the elevated outlier removed. Panel B: Males receiving the placebo who were C. albicans seropositive reported the most bowel difficulties over the 14-week study. C.a.+ refers to C. albicans seropositive; C.a.− refers to C. albicans seronegative. W in the x axis refers to study week. Error bars designate standard errors of the mean for each group at each time point.