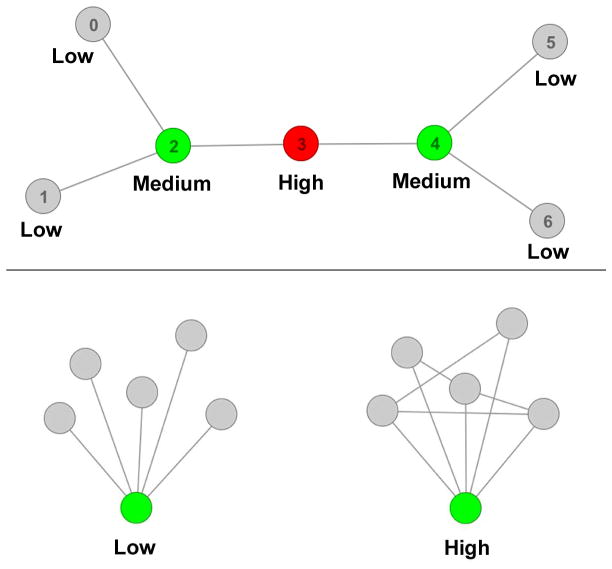
Fig. 1.
Top: Graphical illustration of betweenness centrality. Betweenness centrality is defined as the proportion of shortest paths of a network that contain a given node. Nodes with low betweenness centrality are colored in gray, nodes with medium betweenness centrality colored in green, and the node with the highest betweenness centrality colored in red. Node 3 (the red node) participates in the highest number of shortest paths between each pair of all other nodes in the network and therefore has the highest betweenness centrality. In the present framework, nodes represent brain regions and edges represent connections between regions. Bottom: Graphical illustration of local efficiency. Local efficiency is a measure of ability of a node and its neighbors to transfer information between themselves. The graph on the left has low local efficiency of the green node and its neighbors. The graph on the right has high local efficiency of the green node and its neighbors due to increased connections between the neighbors.