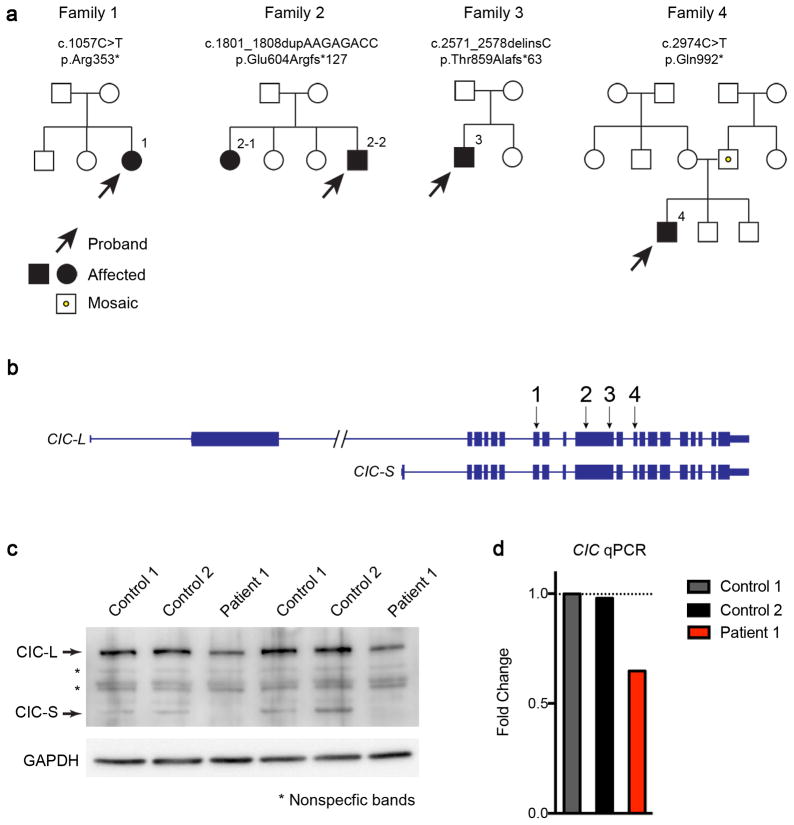
Figure 6. Identification of heterozygous CIC truncating mutations in four families.
(a) Pedigrees of four families with CIC truncating mutations. Both patients in the second family have the same mutation, but neither parent harbors the mutation in their somatic DNA; one of the parents is presumed to be germline mosaic. Sanger sequencing of the CIC variant regions in the two unaffected siblings revealed they do not carry the same mutations in CIC. The father in the fourth family is a low-grade somatic mosaic as demonstrated by Sanger sequencing. (b) Genomic locus of human CIC showing the location of the mutations found in the four families. All four mutations are predicted to create premature stop codons. (c) Western blot analysis of fibroblasts from patient 1 and two controls showing that CIC protein levels were reduced in the patient. Images were cropped for better presentation. (d) qPCR of CIC from patient 1 and control fibroblasts showed that the RNA levels of CIC were reduced in fibroblasts from the patient. The expression levels were normalized to control 1, and fold changes were plotted. Five to six technical repeats were performed for each sample.