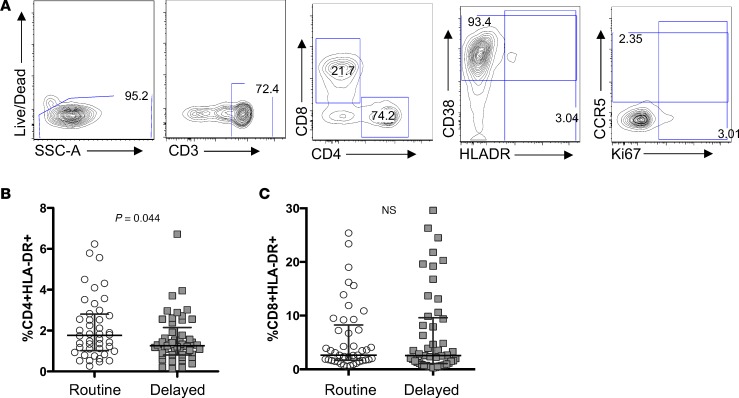
Figure 2. BCG vaccination of HIV-exposed infants is associated with an increase in activated CD4+ T cells.
(A) Representative flow plot depicting gating strategy for determining the frequency of CD4+HLADR+ cells of total (B) CD4+ and (C) CD8+ T cells in routine (circles; n = 45) or delayed (squares; n = 49) BCG-vaccinated infants at 6 weeks of age, when only the “routine” arm had received vaccination, while the “delayed” arm was unvaccinated. Only samples with >1,000 live CD3+ cells were included in the analysis. Lines depict medians; whiskers depict interquartile ranges.