Figure 2. β‐Adrenergic regulation of K+ channels during cardiac AP.
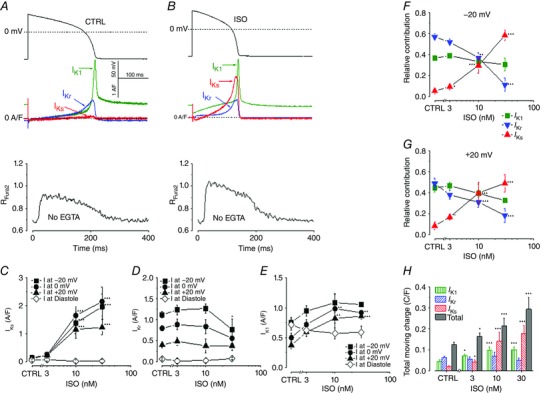
A, AP‐clamp Sequential Dissection experiments were performed as followed: steady‐state APs were recorded at a pacing rate of 1 Hz (upper panel), and used as the voltage command to obtain AP‐clamp recordings of the (three distinct) K+ currents in the same cell (middle panel) and the Ca2+ transients (lower panel) under physiological conditions. B, the effects of isoproterenol (ISO) on the AP waveform and the evoked K+ currents. At 30 nm, ISO significantly enhanced I Ks, moderately increased I K1, but slightly decreased I Kr. C, D and E, concentration‐dependent effects of ISO on the peak densities of I Ks, I Kr and I K1. F and G, the three K+ currents, measured in the same cell, were summed and each current was then normalized to this sum to calculate the relative contribution of each to the total K+ influx. The normalized current values at membrane potentials of +20 mV and −20 mV are shown in F and G, respectively. The ISO dose–response curves show how the relative contribution of each current shifts with various levels of β‐adrenergic stimulation. H, total K+ charge movement for individual K+ current and the sum of the currents during the AP. (Adapted from Banyasz et al. 2014 with permission.)
